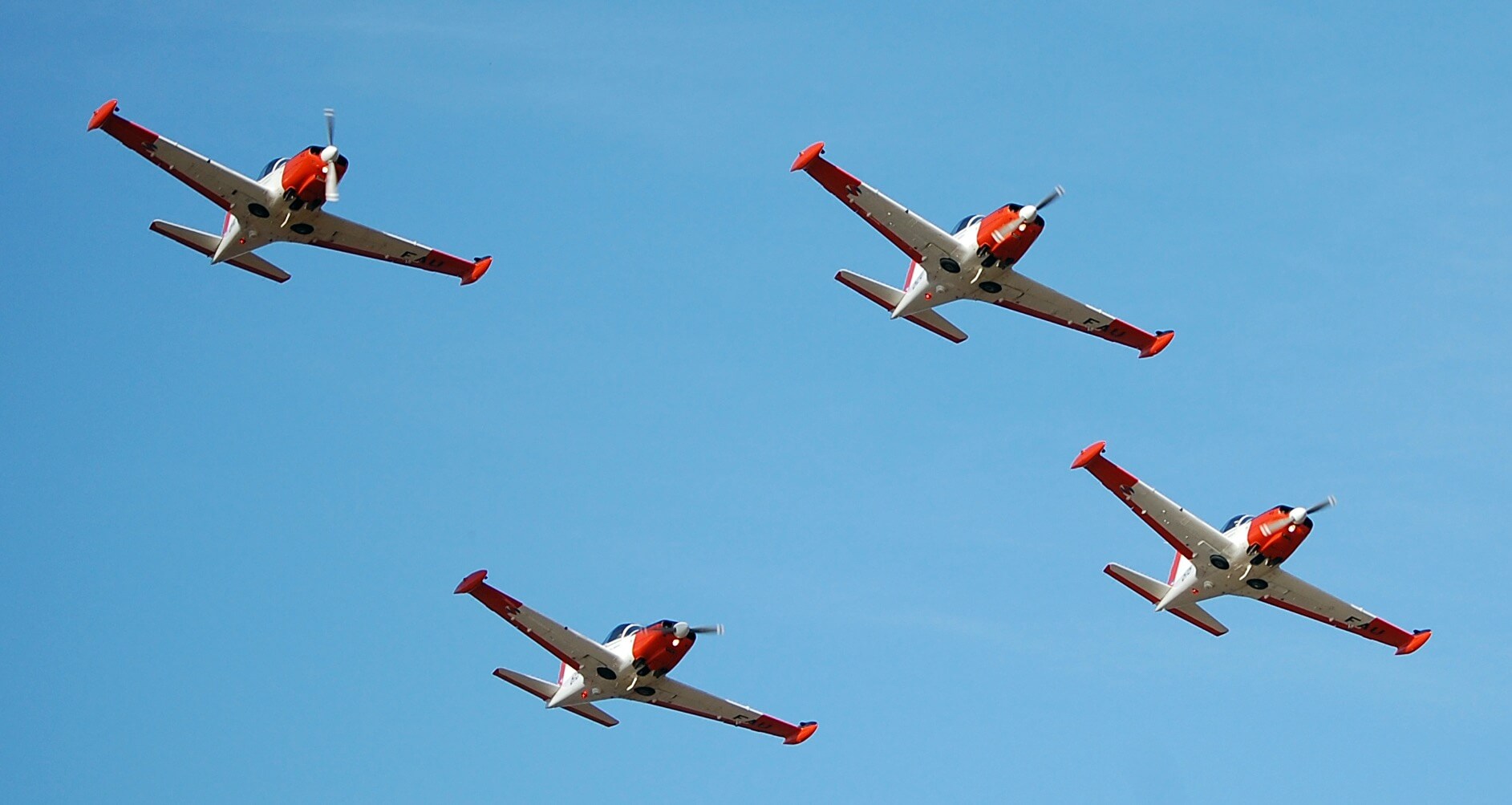
Written in the year 2000 when the SF-260EU fleet was brand new, here’s a relaunch of the feature to celebrate its first 25 years of operation with the Uruguayan Air Force. One of the last aircraft types to have been acquired new and straight from the factory, it was a great occasion at the time for a nation unknown for spending large sums on defence – and with no replacement in sight – the italian trainer will have to continue to offer sterling service to this South American air arm for the time being; forza SF-260EU!
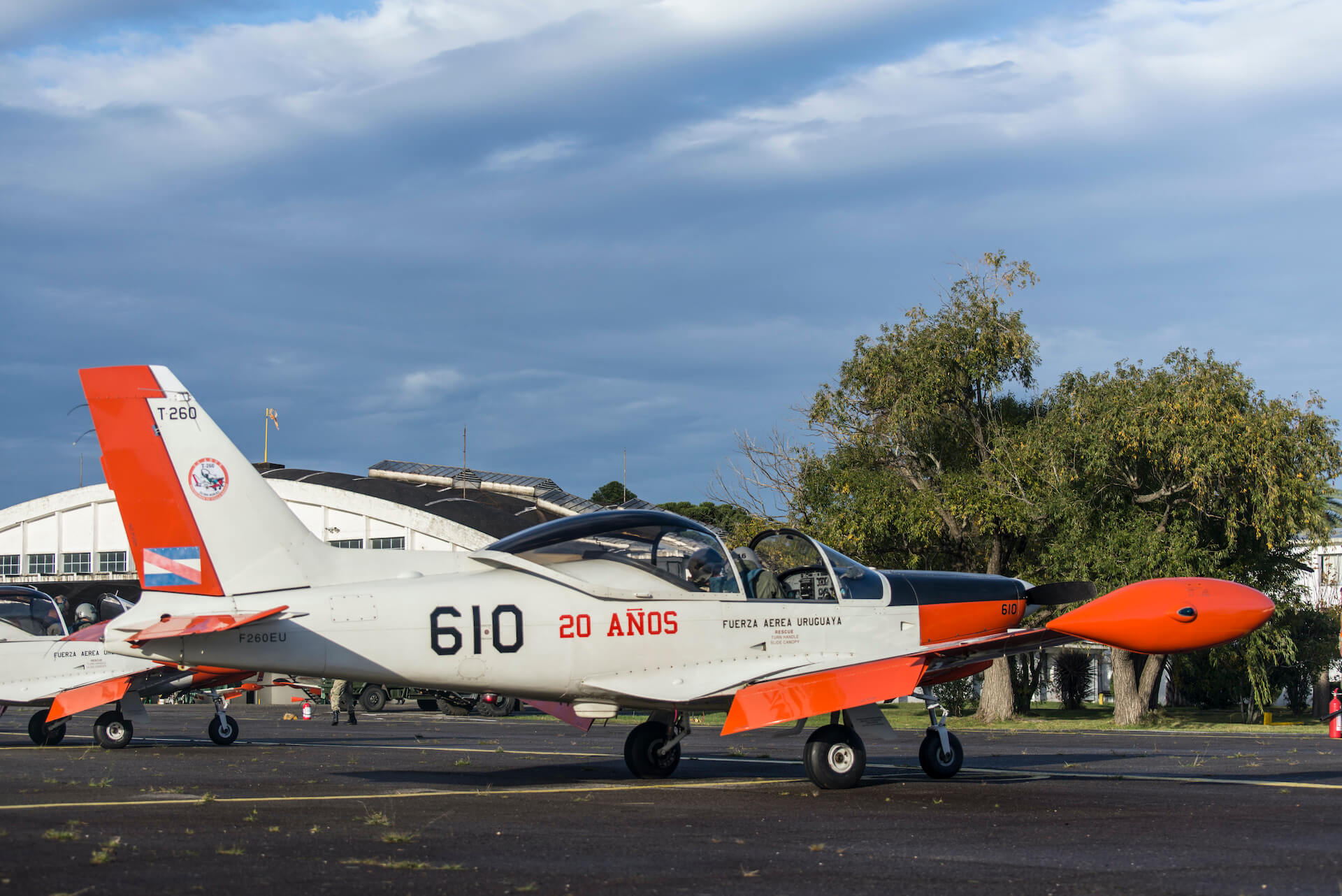
Ernesto Blanco Calcagno flies this Italian built trainer, Alenia/Aermacchi SF-260EU, much loved as a military trainer

Copyright Ernesto Blanco Calcagno/www.airpressman.com
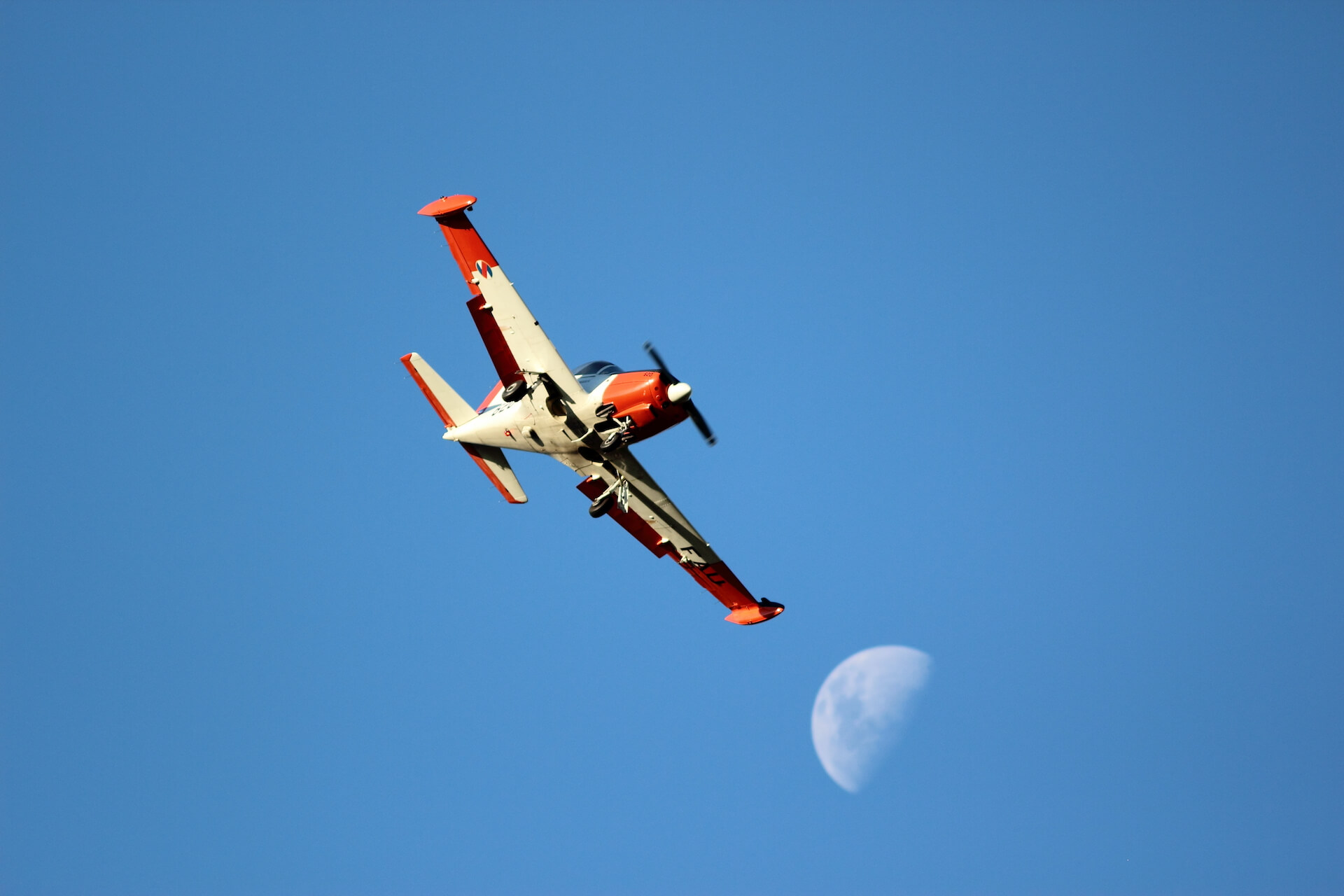

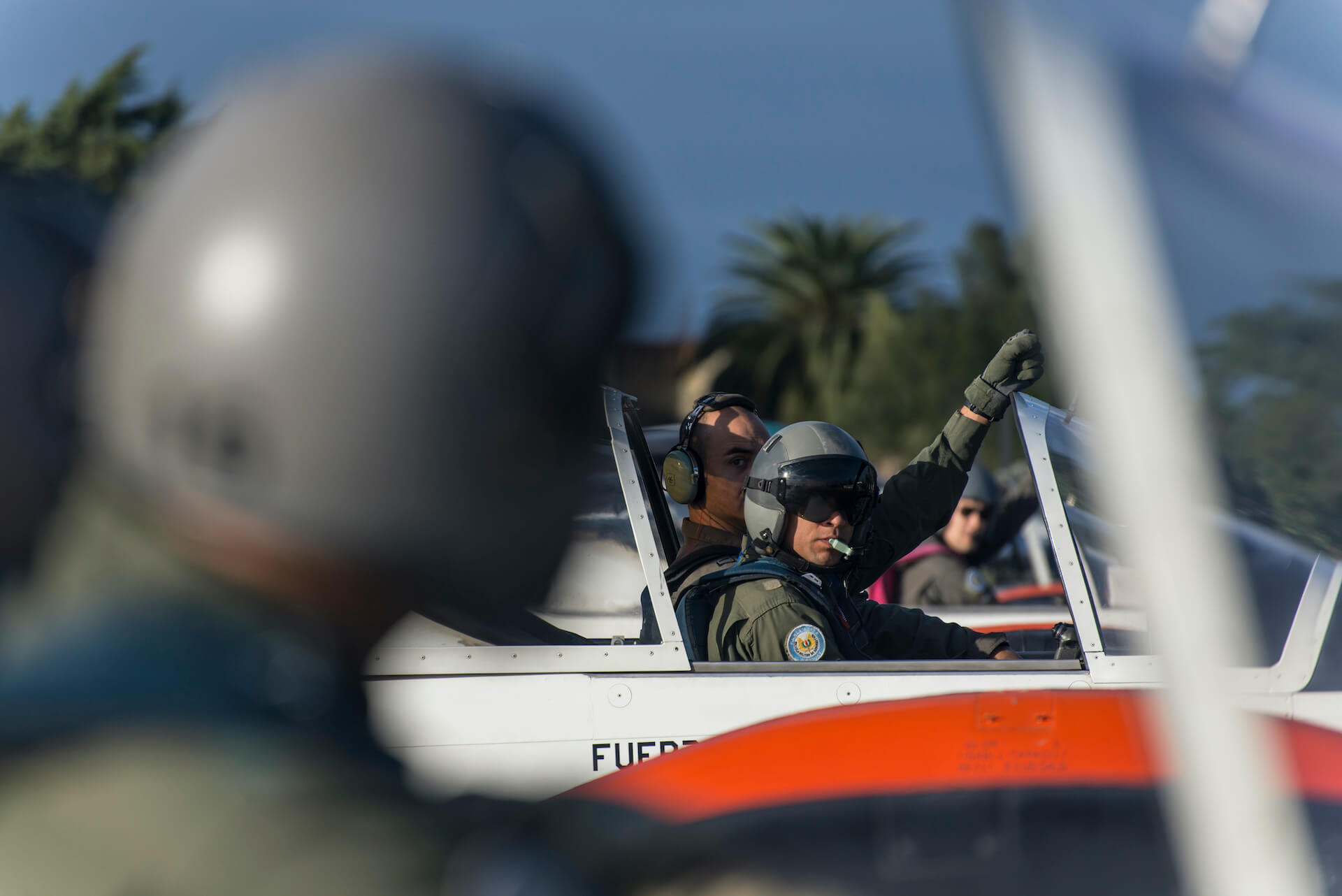
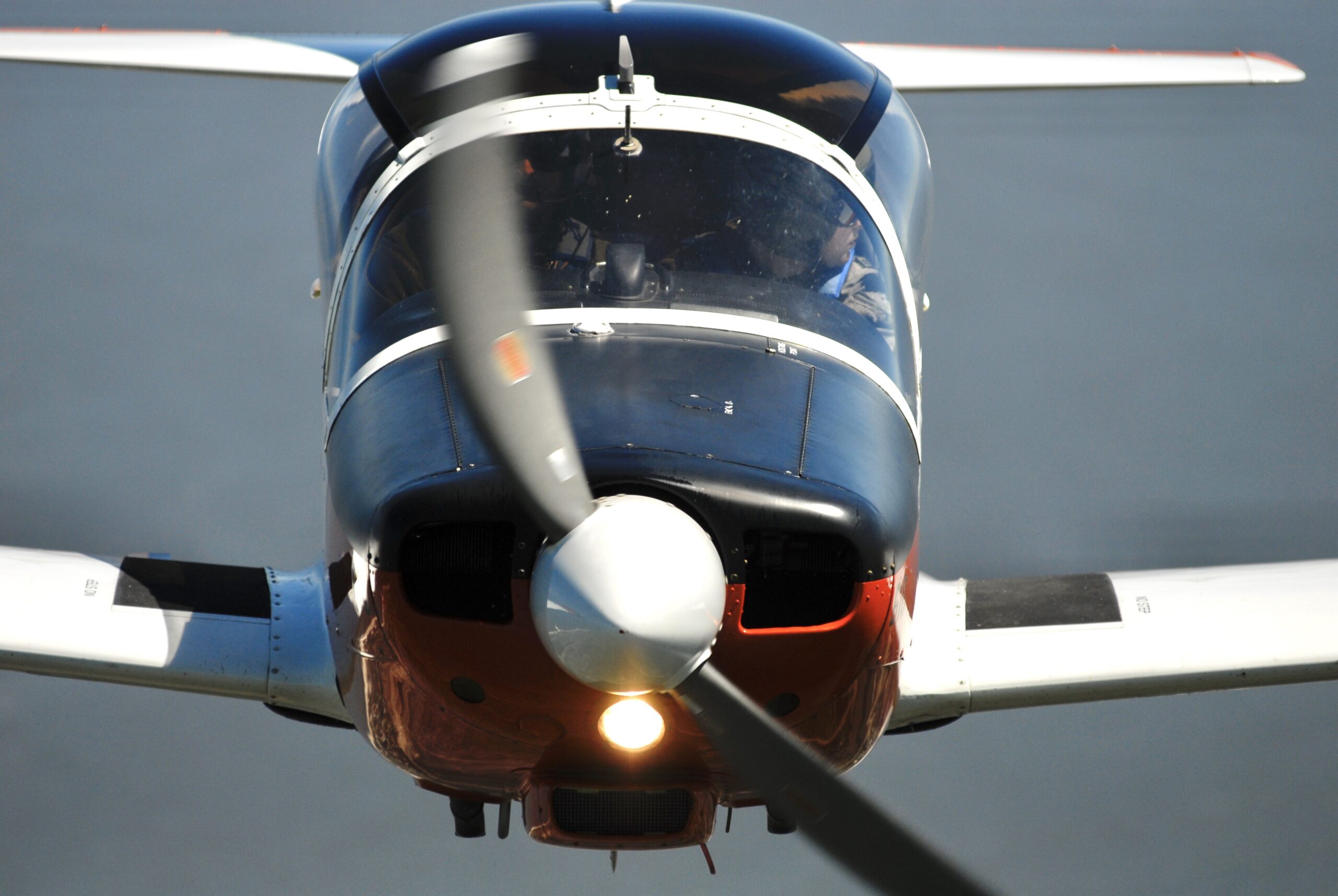
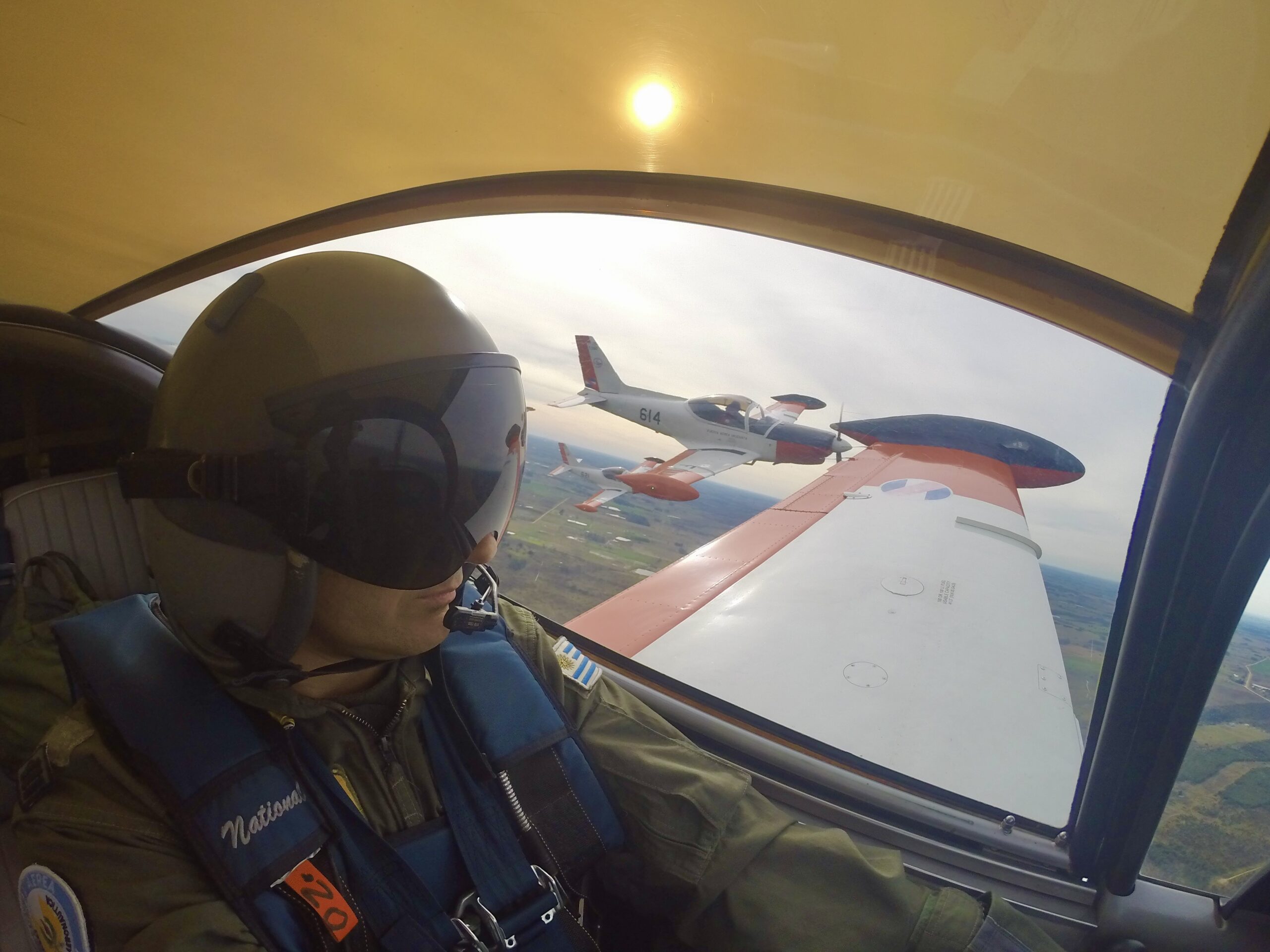
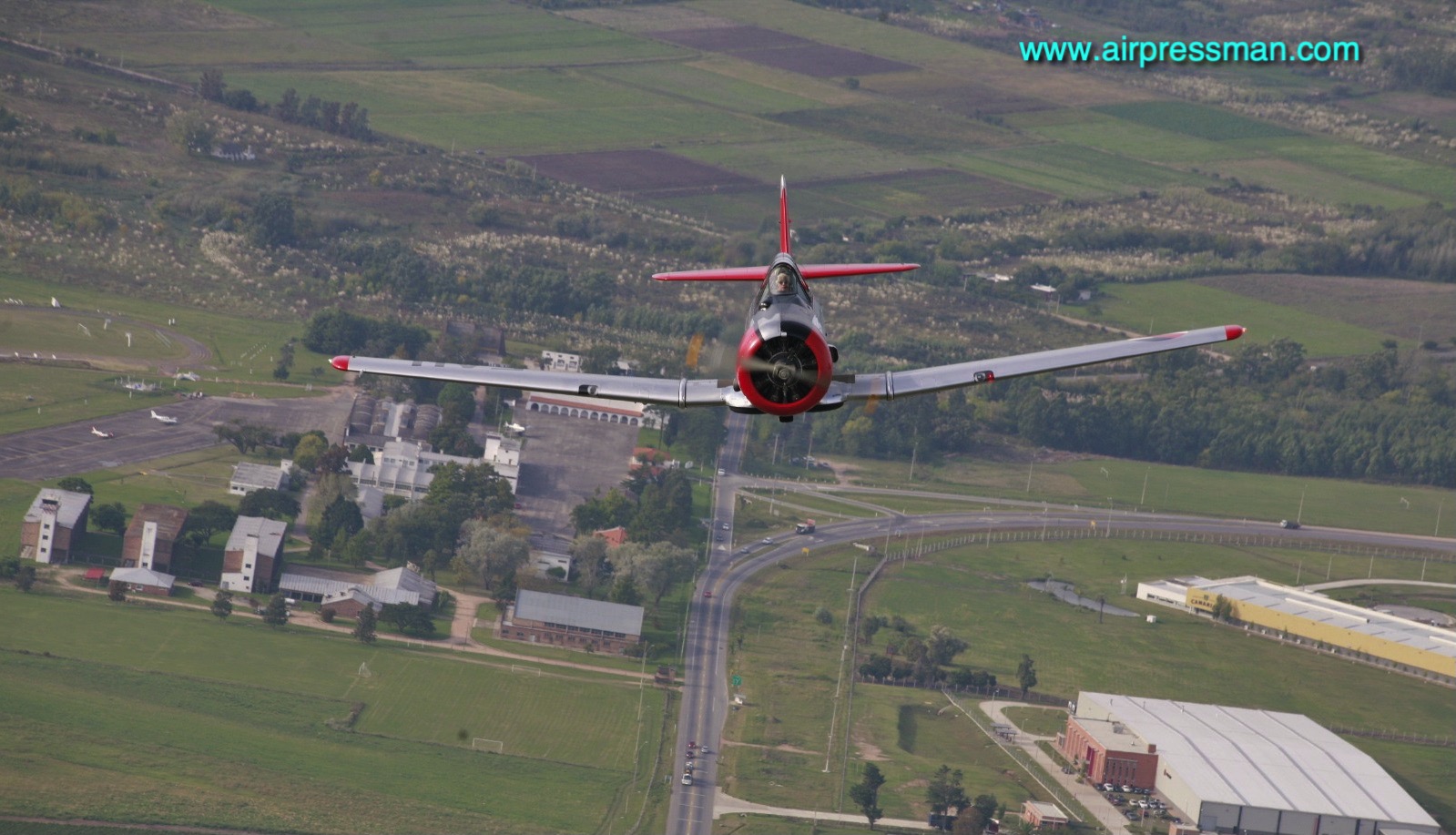
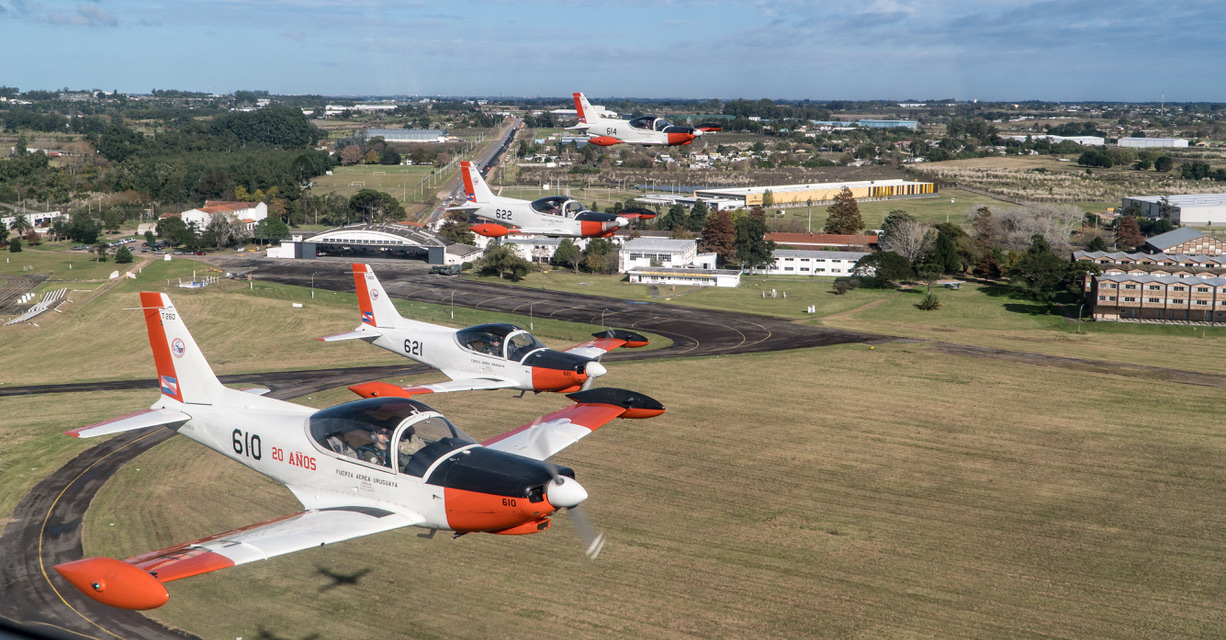
“Do you want to do some loops?” my companion asks.A swift “Yes!” is my reply, and at 180 kt I start a 3G pull-up, as briefed.Blue skies fill the windscreen, but as my neck stretches back, seeking the horizon, green fields and streams come into view as I complete the loop. I’m at General Artigas Air Force Base, home of Uruguayan Air Force (FAU) Academy (Escuela Militar de Aeronáutica: EMA) – to flight test its latest recruit, the Italian-built Aermacchi SF-260 EU.
Captain Juan Villamil, then Chief Flying Instructor of the EMA would be my mentor for the day. He trained for over 2 months with the Aeronautica Militare Italiana (Italian Air Force) and its 70 Stormo/Gruppo 207 (Squadron/Group) in Latina, near Rome in Italy. Here at the Enrico Comani aerodrome he carried out the examiner and instructor course for the SF-260EU, achieving 50 flying hours on the bright orange – at the time – SF 260s in italian service.

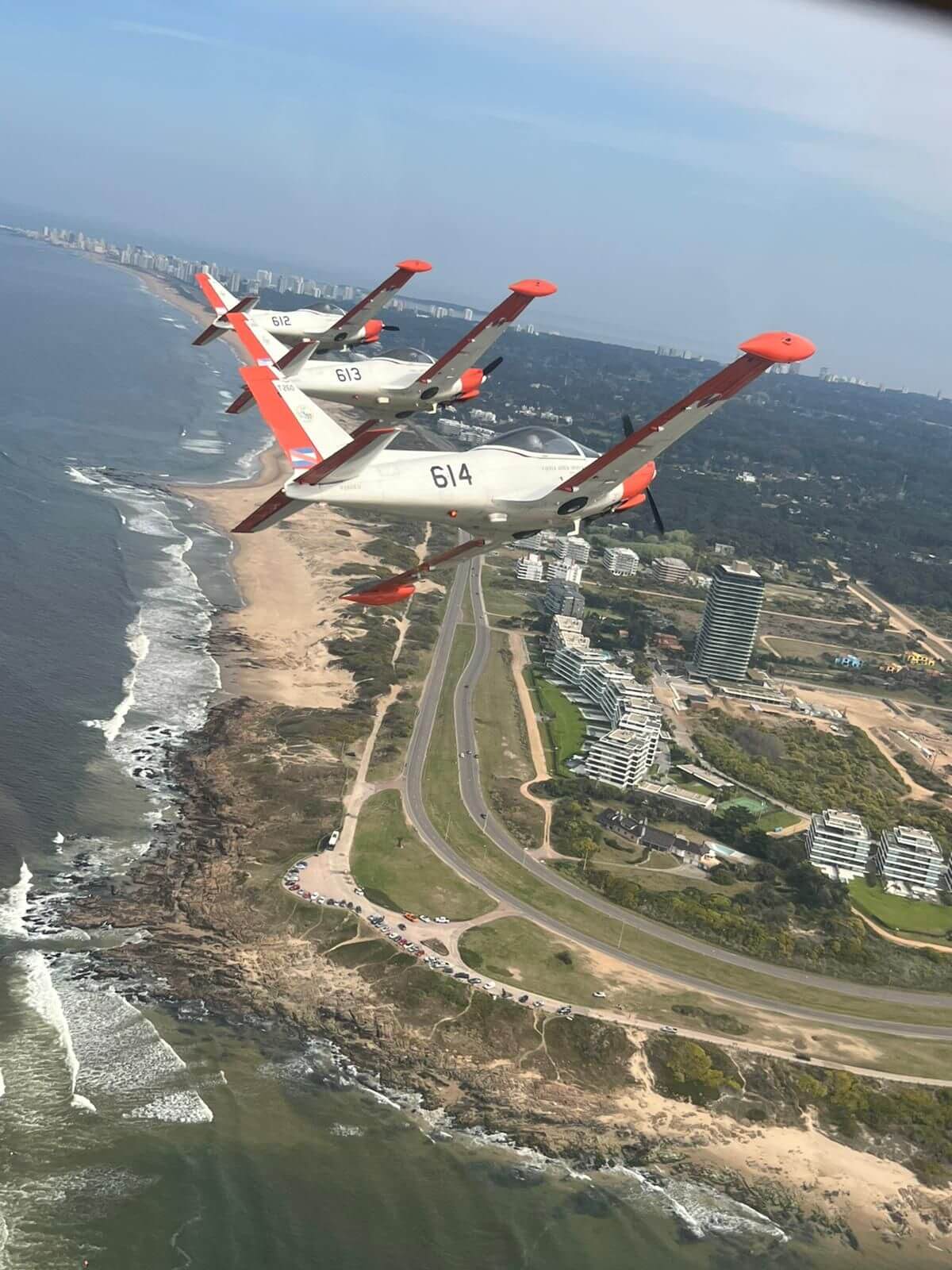
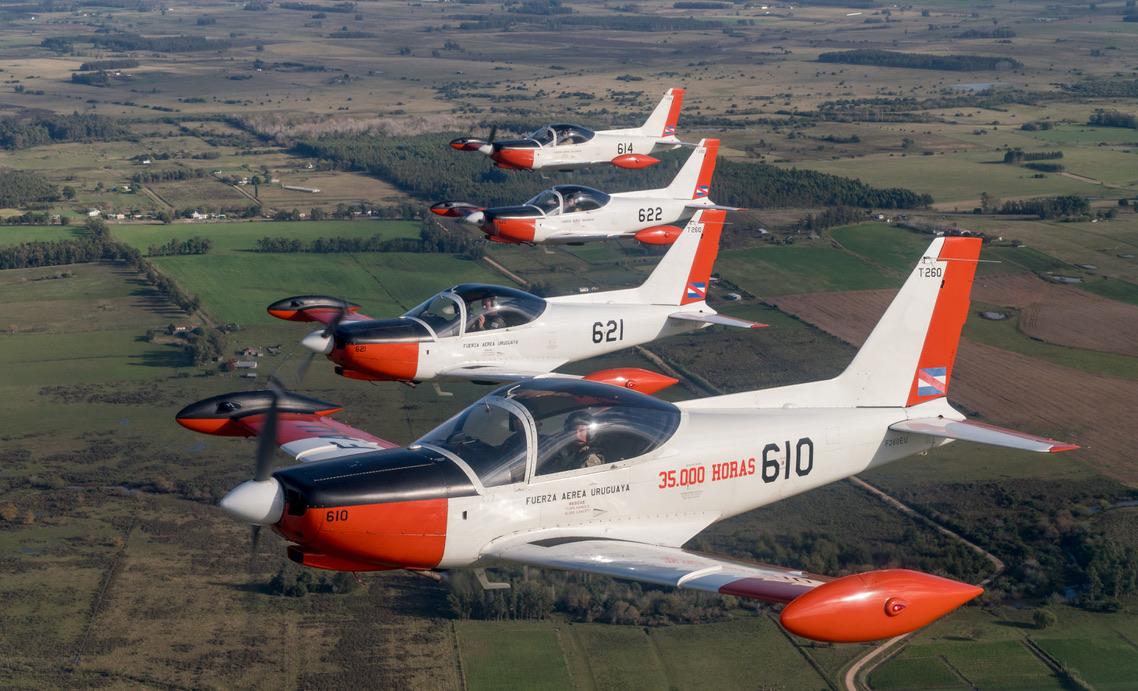
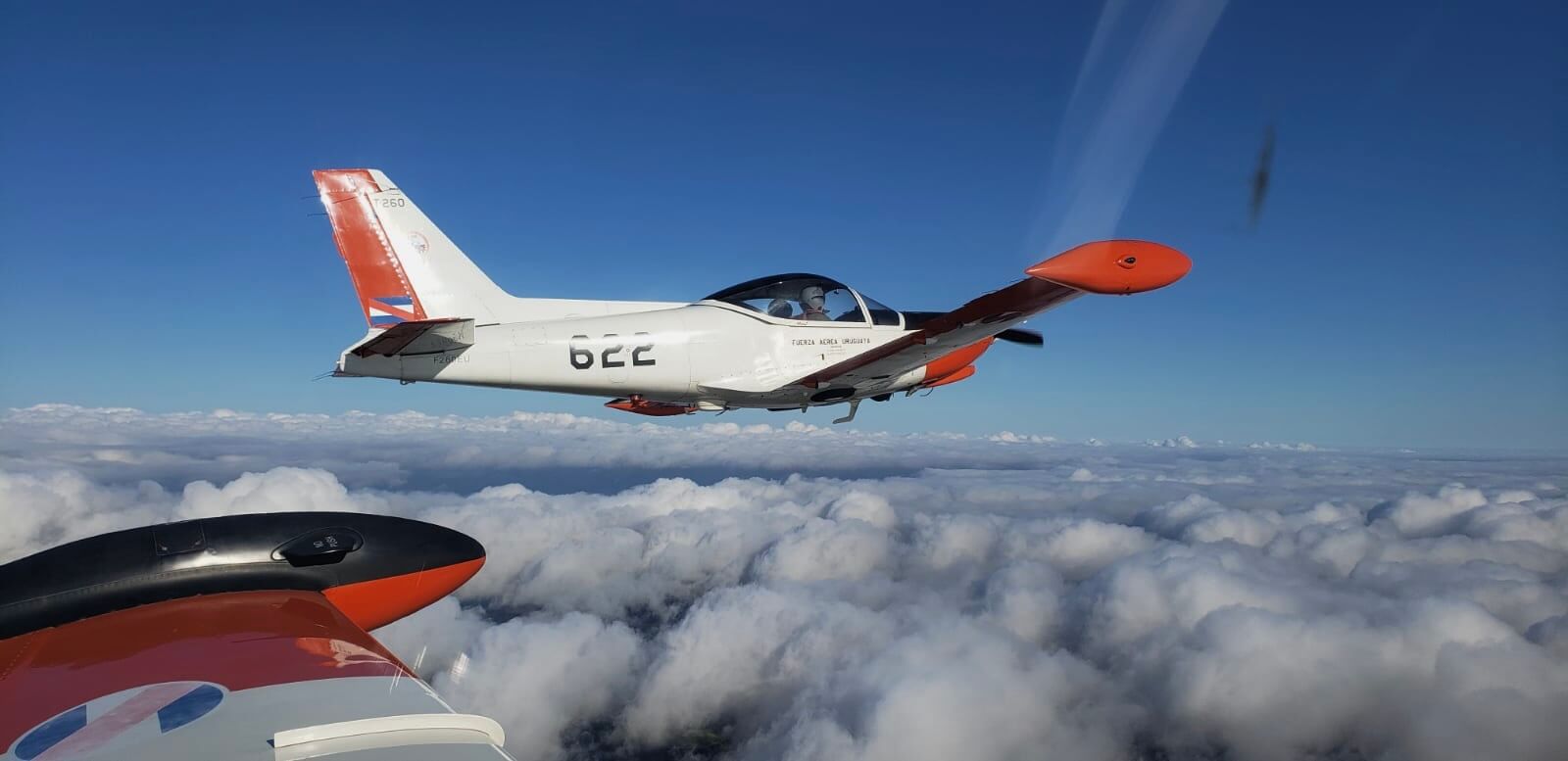
The SF-260EU (E model – U for Uruguay) flown for this report is one of 13 ordered by the Fuerza Aérea Uruguaya (Uruguayan Air Force – FAU) in 1999 to replace their ageing mixed fleet of venerable and ubiquitous Beechcraft T 34A/B Mentor and Cessna T-41D “Mescalero” aircraft. The FAU nominates the Italian type T-260 with the fleet based at Escuela Militar de Aeronáutica (EMA – Aeronautical Military School) alongside the Escuadrón de Vuelo Básico (Basic Flight Squadron) and employed on initial pilot training at General Artigas Air Force Base near the town of Pando, 37 km (20 miles) east of Uruguay’s capital, Montevideo.
REPLACEMENT FOR TWO OLDER TYPES
Since 1969 and until 2000 Uruguayan cadets flew the Cessna T-41D “Mescalero” (a Cessna 172 on “hormones” with a 210 HP Continental and a constant speed prop) for the fundamentals and transitioned, for the advanced part of their course, to the T-34A/B or “glorified” Bonanza as some like to call the Beechcraft planes.
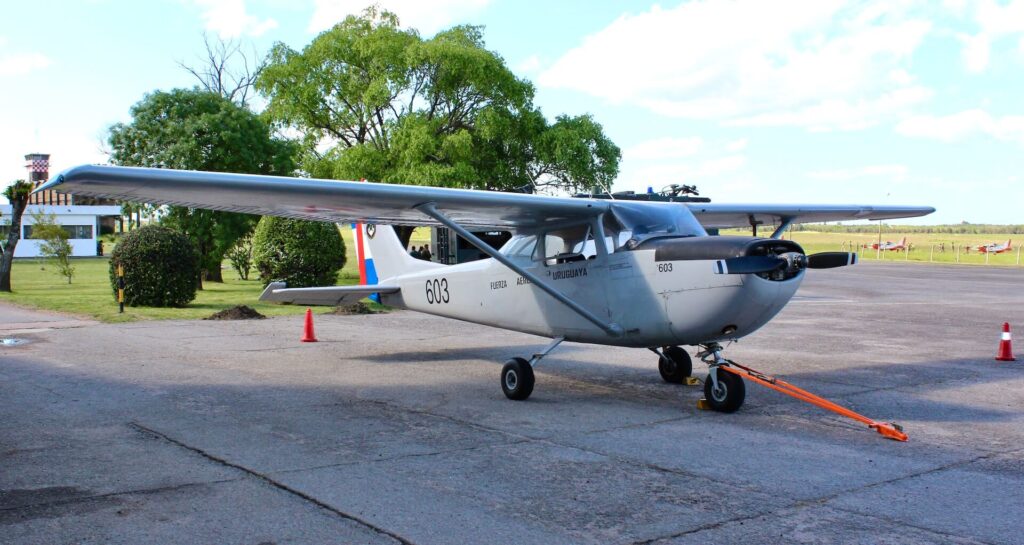

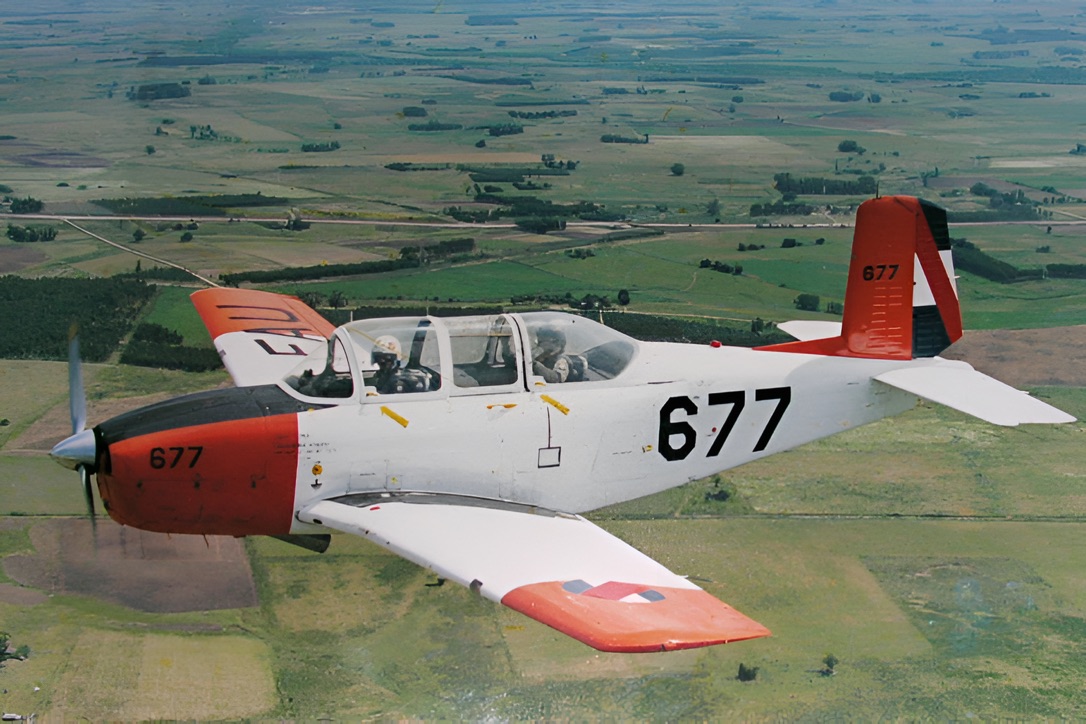
From August 1999, when the first two SF-260EU arrived in Uruguay by ship, they were quickly assembled by the FAU’s Maintenance Brigade at “Brigada Aérea 1” in Carrasco (adjacent to Montevideo’s International Airport) and immediately dispatched to the EMA, and put to use on that year’s pilot course. The T-34s were donated to the Bolivian Air Force (FAB) and some ended up with the Argentine Air Force (FAA) attached to the Escuela Militar de Aviación in Córdoba designated as B-45. The first four flew home in July 2000, with Bolivian officers, after qualifying on the type with the EMA’s instructors. Escort was provided by a formation of five SF-260s till the city of Salto in the northwest of the country, bordering Argentina, by the Uruguay River. A fitting farewell to the Mentor in FAU’s service since 1977. Indeed the FAU has long supplied Bolivia with flying equipment, initially in the 60s with surplus F-51 “Mustangs” and later with batches of Lockheed T 33s. Interestingly, the first women military pilots ever graduated from a South and Central American country (on December 18, 2000) where Uruguayan, having managed to log a few hours on the SF 260, after beginning flight training on the T 41 and T 34A/B.

TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION & PRE-FLIGHT
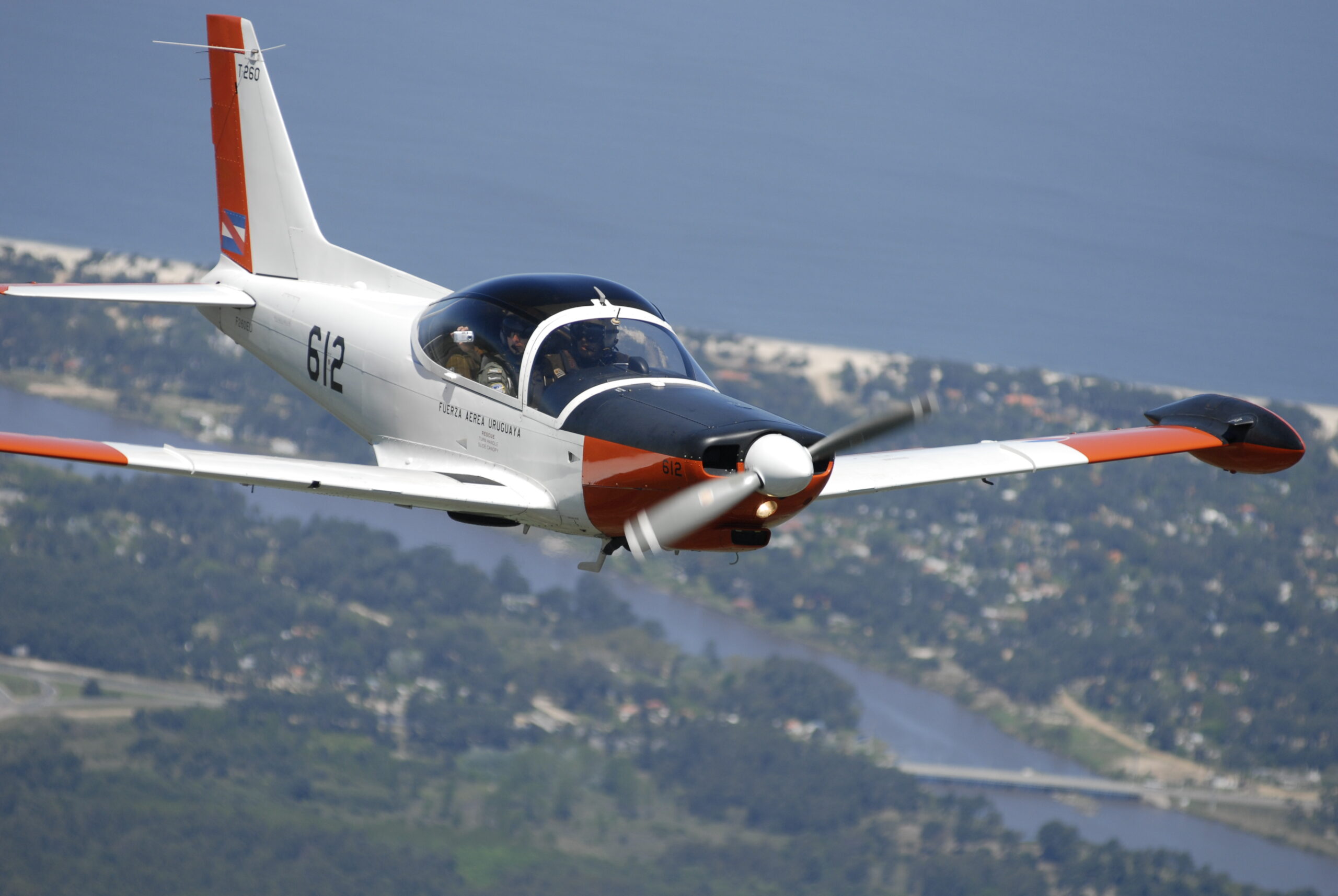
We proceeded with Juan to get kitted out with dorsal parachutes – some very colourful Mistral 145s – atypical to the surroundings and in sharp contrast with our olive green flight suits. Walking towards the “linea muerta” (flight line) I managed a first glance of FAU 612 (S/N 2003). Her good looks provided by a sleek, tall and thin tip tanks, snout up in the air as if ready to take to the skies, soft curves of the canopy, confronted by such a style and remembering the old adage “if it looks good……” I was sure this elegance exuding craft would fly nicely.

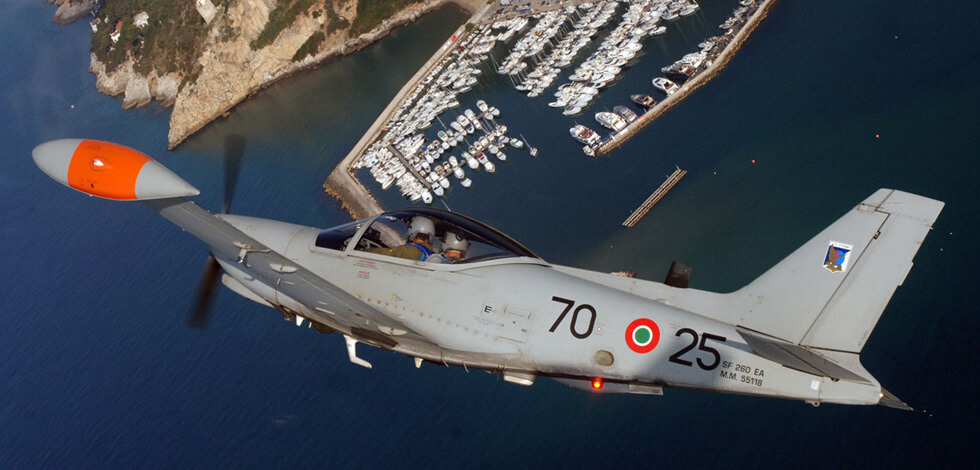
The SF 260EU is an all metal, semi monocoque, low/laminar flow wing, cantilever airplane, tricycle, with a retractable undercarriage fitted with oleo pneumatic absorbers. Power is supplied by a continuous flow injected 260 HP Textron Lycoming AEIO-540-D4A5 having a six cylinder, horizontally opposed, air cooled arrangement. An all metal, two bladed Hartzell constant speed prop (HC-C2YK-1BF/F8477-8R) completes the front end. Before deciding for the italian trainer, the FAU considered and tested the Chilean ENAER T-35 “Pillan”, Moravan ZLIN 242 from the Czech Republic and the French Aerospatiale “Epsilon”, together with the SF 260E. The latter was chosen as it achieved a good balance between performance, reliability, maintenance costs and factory support. Juan reminded me that the E version of the Aermacchi machine had been one of the contenders for the United States Enhanced Flight Screening aeroplane, the triumphant one becoming responsible for checking out bidding USAF pilots. The British Aviation Slingsby T-3A “Firefly” was the winner, a decision some US officials off the record said it was a political one. Unfortunately three crashes lead to six dead and the USAF permanently grounding their 107 planes (and a $32.4 million investment) in October 1999. A lengthy flight test program at the famous Edwards AFB detected ten problems of mechanical nature with the aircraft and its engine.


Whilst Juan continued with straightforward exterior inspection, I’ve got a helping hand with my parachute from one of the technicians. Having to crouch slightly forward to connect the two parachute leg straps into the front buckles, I become the object of jokes, as the technicians explained, what might happen to certain parts of my lower, uniquely male anatomy, if caught on the straps. I was told to ensure proper placement of the harness underneath one’s crotch as considerable pain might come to me in case of a bail out and consequent parachute opening! Cockpit access is Access via black non- slip wing panels fitted on both sides. The canopy slides longitudinally backwards, and can be operated by means of an upper latch. An emergency canopy release red “T” handle is fitted underneath and to the left of the engine control quadrant (standard from the model D upwards).

COCKPIT
A third seat is located centrally behind the two forward ones (access to the battery and electronic equipment bay is possible through this area seat as its seat back detaches). This arrangement could allow for the carriage of a further student, either pilot or navigator, increasing immersion into the syllabus being taught, however a parachute cannot be worn by the seat occupant. I was offered the right seat that for many air arms, the selected seat for the pilot in command, in this case for the student. In the right seat you have the throttle, prop and mixture control levers close to your left hand – in military fashion – as on the left seat only the throttle lever is duplicated, for the instructor to handle. This is a first in Uruguay (the T-34 had tandem seats, as did previous trainers in Uruguayan use, as T-6s “Texans”, PT-19s and “Chipmunks” before that) and this lever array will put the future officer at ease when transitioning to advanced training and the squadrons. Upon graduation ensigns spend one year flying the Swiss built Pilatus PC-7 at the EVA (Escuela de Vuelo Avanzado – Advanced Flying School) at the Brigada Aérea No. 2 (Air Brigade 2) in Durazno 181 km (98 miles) north of Montevideo and a few lucky ones will receive orders to join combat squadrons equipped Cessna A-37B “Dragonfly” and from 2025 Embraer A-29 Super Tucano. (Check the A-37B features here A-37B “Dragonfly” – Post Maintenance Fly Test and A-37B ROAD DEPLOYMENT: “Highwaymen”Martin Baker Ejection Seats-Safer life for an old jet.
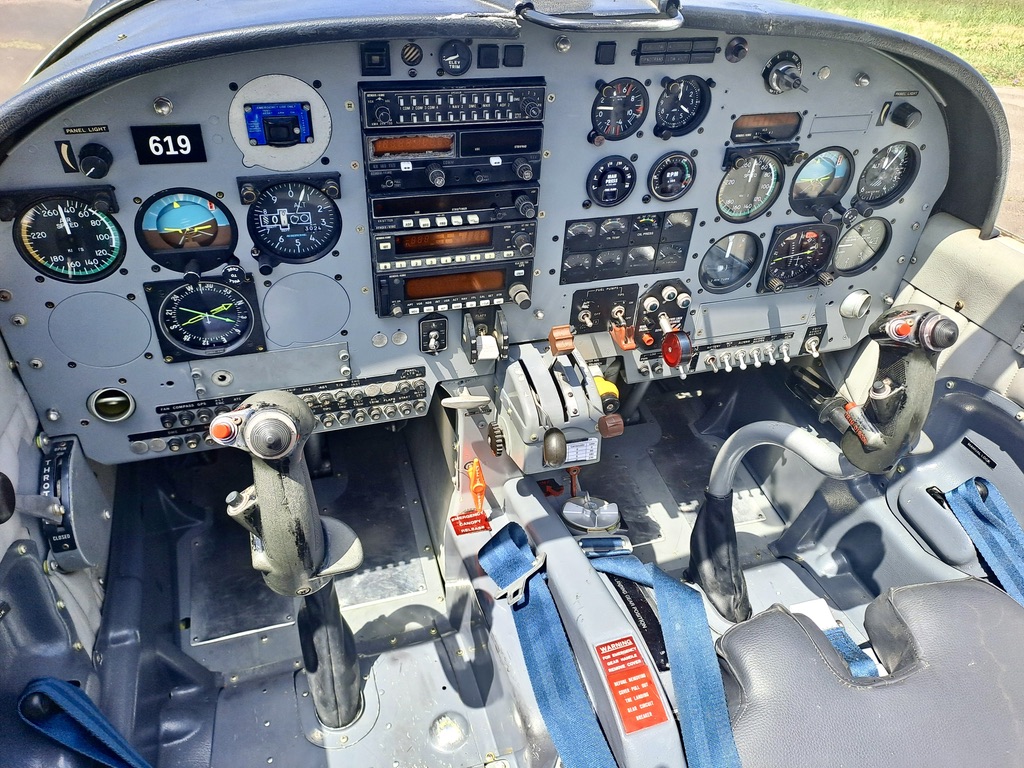

Forward seats adjust fore and aft on a metal rail fitted beneath the middle of the seat (older SF 260s had a rail either side) and forward of this rail is where you would find an air conditioning vent, if you selected this optional extra (not installed by the FAU). The set, combined rudder pedals/toe brakes come within easy grasp once your seat has been attuned to your liking. The rounded seat backs allow proper fitting of the back parachute and can be fold forward to allow access to the rear seat. A five -point inertia reel safety belt and shoulder harness, fitted with a quick release mechanism plus an outboard installed inertia reel control lever (allowing for the locking of the harness before take off, landings or when required) completed the seating area. The cockpit is of a conventional design. A mixed of pragmatic mechanical and digital displays are fitted, a consequence of the old cockpit design being updated to carry more modern instrumentation.
My attention was caught by some of the engine instruments. The combined manifold pressure/fuel flow indicator has an upper LED barograph (fuel/air mixture readings are taken from the no. 5 cylinder manifold) and a lower indicator providing a digital readout of the fuel flow.
The tachometer comprises two types of digital indicators: a dial and a numerical one on a small lower screen, making it easy to set rpm precisely. If you over do the engine RPM (engine over speed is defined as 2750 and above for longer than 3 seconds) the digital indicators will flash for 10 seconds. More contemporary indicators like cylinder head temperature, oil temperature, oil pressure and alternator load are aptly installed below the instruments mentioned above. Thus getting a good idea of the well being of your engine at glance, useful when performing aerobatics or whilst in formation and the same can be said for the adjacent accelerometer and the stall warning light. Reminders that you were on a military machine came in the way of a “canopy breaker” (a thick black titanium short bladed knife) fitted beneath the right electrical switches panel, and a centrally located canopy cabin/map spotlight which can also be used for intermittent light signals, in case of having a bad day with your radio equipment.
FUEL SYSTEM
Complexity to a light aircraft of this sort is added by means of several switches on a fuel pump control panel and ancillary indicators and warning lights fitted for the semi automatic fuel management. A fuel shut off cock is attached to the firewall and on the cockpit’s side it’s controlled by a red lever below and to the right of the control pedestal, lockwired in the open position. Older SF 260s had a fuel selector centrally below the throttle quadrant. Three electrically activated fuel pumps are fitted, (not counting the engine driven pump) auxiliary 1 and 2 (both bolted to the fuselage adjacent to the aft left wing root area) plus a single tip tank transfer pump (bolted to the right wing root area) for the two integral, non- ejectable, 72 litres/19.02 USG fuel wing tip tanks. Pumps AUX 1 and 2 are essentially the same as both draw fuel from the main 49.5 litre/13.08 USG tank on the left wing and supply it to the Lycoming. These wing structure vented fitted tanks (also one on the right) hold 49.5 litres/13.08 USG each and have anti sloshing frames (including the tips) expected on an aerobatic machine.
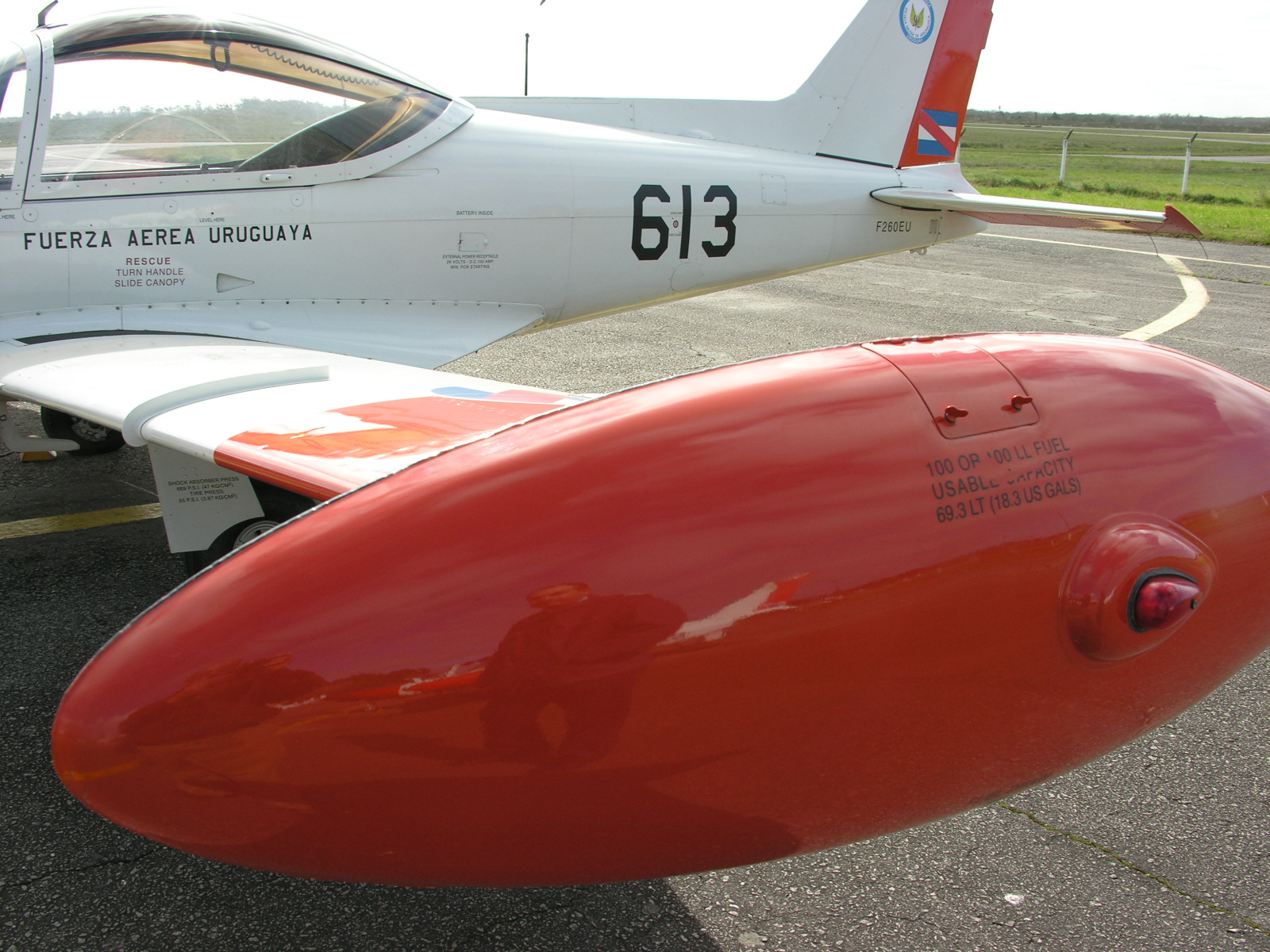

tip tanks. (Picture by Pilotoviejo)
The transfer sequence is obtained by pressure differential, starting from the handsome, aluminum alloy tip tanks, if used. The quality of the aircraft can also be seen on the tank ridges and seams, welded together and filled over for a smooth finish. When both tips are empty (below 5 lb) feeding continues from the right wing tank until a single litre remains, by means of a jet pump into the left wing (main) tank and from here into the engine via the selected “AUX” pump and maize of lines, strainer, pressure switches, engine fuel pump, “Bendix” injector, flow divider, thus a permanent, same pressure fuel flow finally reaching the cylinders on any engine cycle.

NAV/COMM
Flight instruments fitted on the right hand cockpit are an airspeed indicator, attitude indicator, encoder altimeter, 2 min. turn and slip indicator, HSI and a VSI. On the instructor’s side a RMI compass card is supplied. For navigation and communication purposes a suit of Bendix/King equipment has been installed above and slightly left of the throttle quadrant. It includes VHF Comm./Nav. radios, ADF controls and a transponder. DME control and indicator is nicely located above the airspeed indicator, an inch below the ignition switch, on the cockpit’s right. A welcome addition comes in the way of a rectangular KLN89B GPS set. The GPS control panel was now placed on the centre panel below the transponder (unlike below the RMI, as delivered, its view hindered by the control stick) a modification carried out locally in consultation with Aermacchi. Six vacant instrument locations remain available, for future usage if needed. The control stick has the usual practical features, incorporating on its grip the RT “push- to- talk”, ICS call function and trim disconnect switches and a “coolie hat” thumb activated trim switch. An electrically actuated trim tab located on the right elevator provides longitudinal trimming, whilst lateral relief of aileron forces is supplied by an electrical actuator fitted on the control stick torsion bar, that displaces the neutral point of the stick, therefore of the ailerons. Above the NAV/COMM stack, is located the wing flaps indicator. A circular barber pole style display shows diagonal strips during flap transition movement, and when the flap control selector is set to UP, T/O and LD positions – 0, 30 and 60 degrees respectively – displays these indications to the pilot. The adjacent flight controls indicator, assist you to detect elevator trim tab position through a miniature aircraft display, and aileron trim visual feedback comes via the “AIL TRIM” annunciator, which illuminates green when the control stick and the ailerons are neutral. “TRIM RESET” lights up when you press a switch on the lower left side of the control stick, inhibiting trim control. This feature might be used to simulate trim system failure to a student or most likely to disconnect the system in the event of a runaway trim electric motor. Left of these indicators we find an ELT switch light, inoperative as ELTs have not fitted to the Uruguayan fleet. (Author’s note: since then an ELT has been fitted to the fleet. An activation switch is now fitted above the altimeter on the LH seat)
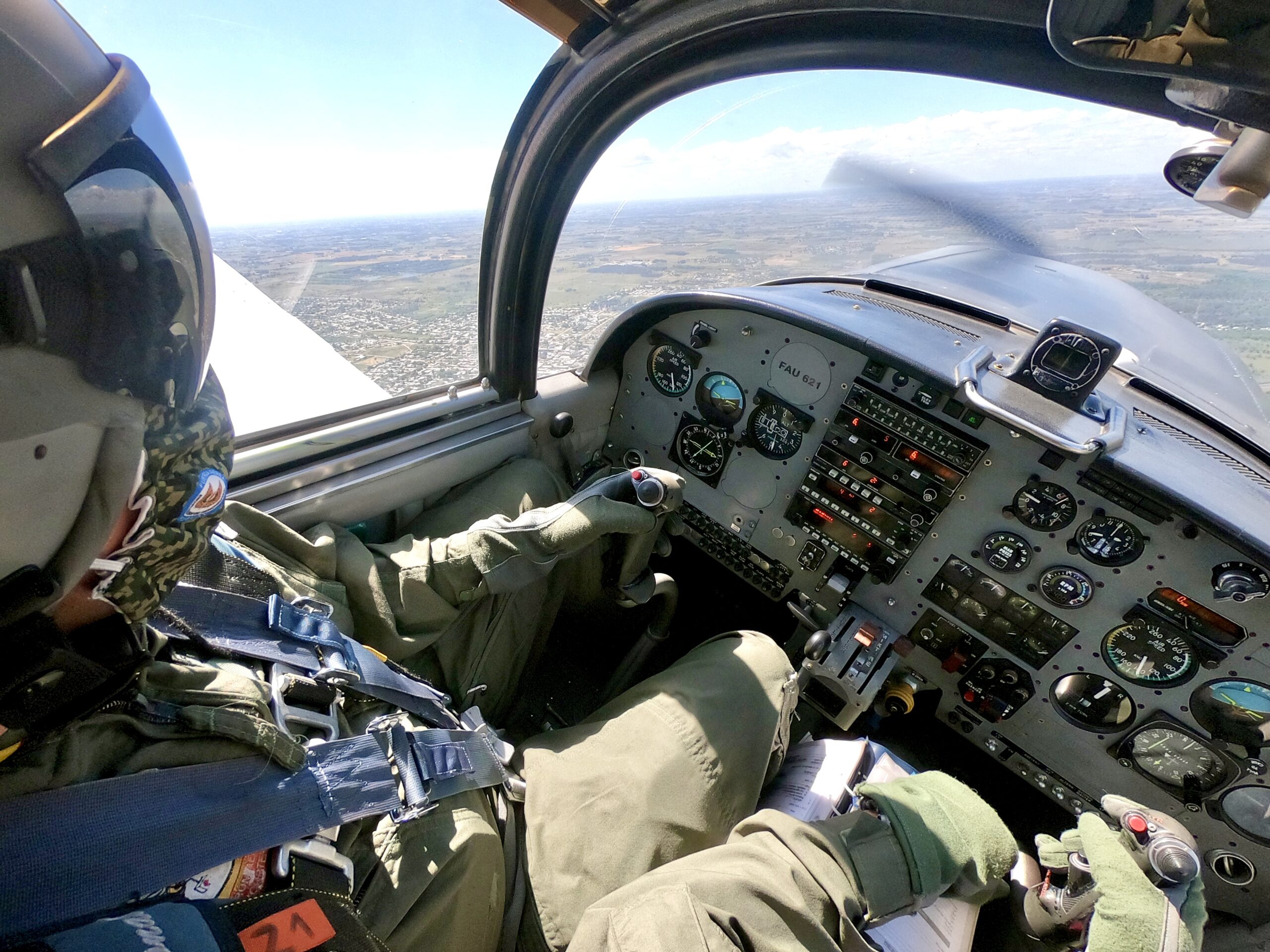

Juan started the 260 HP Lycoming and finally the T 260 was alive. In the open cockpit “Artigas” tower burst into our headsets: “Trébol, Wind 180 degrees 10 knots, QNH 2990 RWY in use 19”. “Trebol” being Juan’s callsign (Shamrock in Spanish) but I never did check for Irish roots on his family tree. I noticed how close to the ground my bottom was (approximately 40 cm/17”) and committed it to memory the forward view and attitude for the landings. The view ahead is very good and the steering system – the nose wheel is mechanically linked to the rudder pedals – quite sensitive to gentle feet input on the combined toe brakes/rudder pedals. No differential braking is required nor advised by the manual. Ground maneuvering shouldn’t be a chore as the nose wheel travels 20 degrees either side and the minimum turning radius is just over 8,5 metres, or the aircraft’s wingspan. Ground roll is a comfortable one on the main 6.00- 6 (55psi) undercarriage and 5.00- 5 (50 psi) nose wheel. Anhydrous nitrogen (water free, I confess had to check!) is used for inflating these low pressure tyres, however if not available dry compressed air usage is permitted. If operation from grass or unprepared fields is required, that with proper undercarriage oleo extension, prop/ground clearance is a decent 35 cm.

Time to stop for engine run up and pre takeoff checks: Idle at 700 RPM and parking brake set (the latter action requires caution as its horizontal handle left of the throttle quadrant, is very close to the red emergency canopy release handle). The balls of my feet slid up to the toe brake pedals and the throttle increased to 1700 RPM. Testing the 2 bladed prop, I increased and decreased the Hartzell’s rpm twice with the ensuing revolutions drop (no more than 500 RPM), and growling sound. We also noted at this time a reduction in oil pressure, indicating oil was flowing to the crankshaft driven propeller governor, which is supplied with engine oil. Power up to 2100 and the black and yellow “alternate air” knob, right of the mixture control, was pulled, noting a further RPM drop as the engine is fed with warmer air from the engine compartment (small adjustments to the air flow can be made by turning the knob).
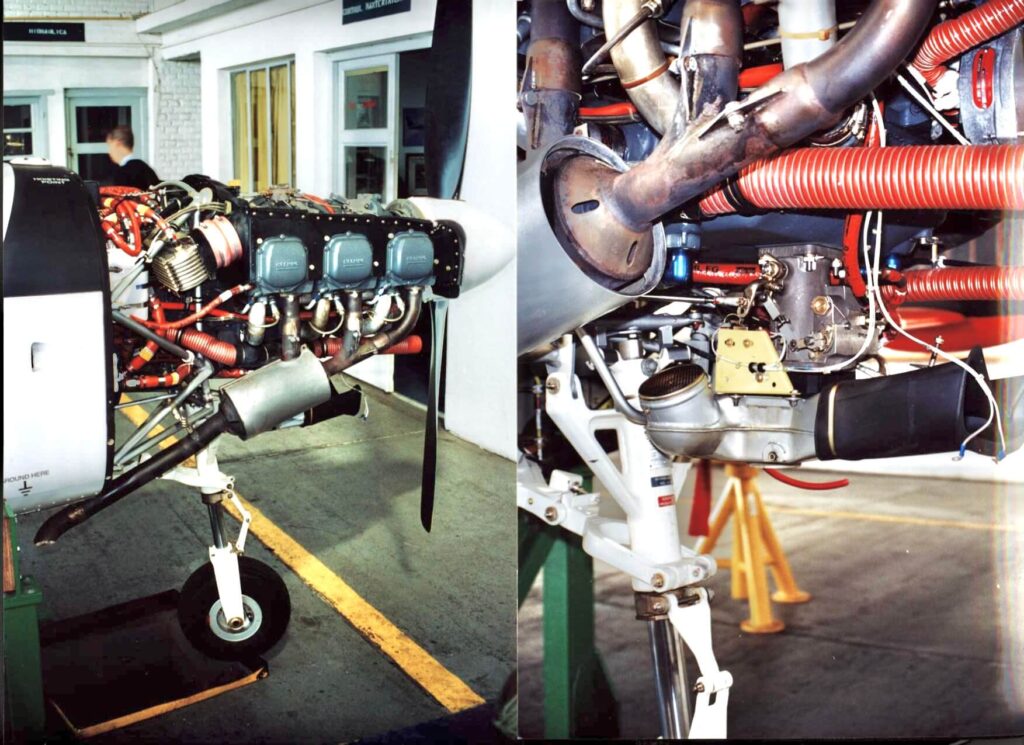
The air induction system is provided with an automatic and a manually operated air intake, via an opening in the cowling lower section feeding an air induction box by means of a rubber duct. In case of air flow blockages the AUTO air intake opens providing air supply to the engine (via a spring loaded valve on the black rubber induction duct upper surface)
The manual also calls for the “Alter AIR” knob to be pulled out when flying in typical IMC conditions, and temperatures ranging from + 5 to – 5 degrees centigrade. The price you pay is a manifold pressure drop of 1 to 2 psi but peace of mind gained as the induction system can gather ice in such parts as bends, impact tubes or air filter.

AIRBORNE!

Mixture on lean to check for an RPM drop (the lever runs on a indented slot, diminishing the possibility of an inadvertent cut-off), back to full rich, magnetos, flaps set to TO (take-off or 30 degrees), a last check of the annunciator panel, control surfaces checked free and correct, cockpit locked and we are ready to wander into the ether. Juan says, succinctly, as we taxi onto runway 19: “You’ll do it”. On the take off run the aircraft’s behavior is light aircraft like, however more spirited than I’m used to. Slow power application is demanded as during rapid engine acceleration the prop governor may allow the RPM to increase and overspeed for a while. The tachometer showed 2650 rpm and at 60 knots, and 14 seconds after power application, with a gentle rotation I placed the nose tangent to the natural horizon, as briefed. Out take off weight was about 2330 lb (1059 kg), a typical load for an aerobatic training mission, my guess is we used 500 feet of runway, with a 12 knots wind straight on the nose.

Checking the VSI for a positive rate of climb, I raised the gear (retracts in 5/7 seconds) and by now we were doing 80 knots, followed by flaps up at a safe height with quite unnoticed trim changes. Juan reminded me to keep the nose just above the horizon until we had accelerated to 110 kt (the flight manual states a 105 kt climb speed at sea level) setting a westerly heading towards the restricted military training area east of the aerodrome (R5 East & West). The airplane felt docile and gentle to handle as well as responsive in all axis. The fixed tail plane and moving elevator pitch authority is good and in no doubt assisted by its horn and mass balance, however I was impressed with the roll response. Each aileron is fitted with a servo tab on its inboard trailing edge, producing a large turning moment thus reducing stick side forces, therefore rolling the aircraft is effortless. It also doubles as an aileron trim described previously (actuated independently of the aileron actuating system) displacing the lateral neutral point of the control stick to obtain lateral trimming.

Juan called for a power reduction to 25 in HG and prop to 2500 rpm and continued the climb at 110 kt and 20 degrees of bank. The negative by products of the spiral propeller slipstream effect and left hand swing produced by the torque reaction and some asymmetric prop blade effect at higher angle of attack, were diminished by design modifications like fitting the engine 2 degrees offset to the right and 2 degrees upwards (“cant” the engine as our American cousins call it) displacing the thrust line in the same direction slightly. Installing the engine 2 degrees up, diminishes a nose down pitching moment born out of the thrust and drag pitching couple. The SF 260 has two axis trim tabs (longitudinal and lateral) operated by electrical actuators. Fixed, ground adjustable, trim tabs in the shape of small strips of metal affixed to the trailing edge, do assist in the correction of rigging problems and fine “tuning” control surfaces, giving a good balance. They can be seen on the outboard end of both ailerons and the upper rudder section. The rudder is horn and mass balanced as well and the top section of the fin houses the VOR/ILS antennas.

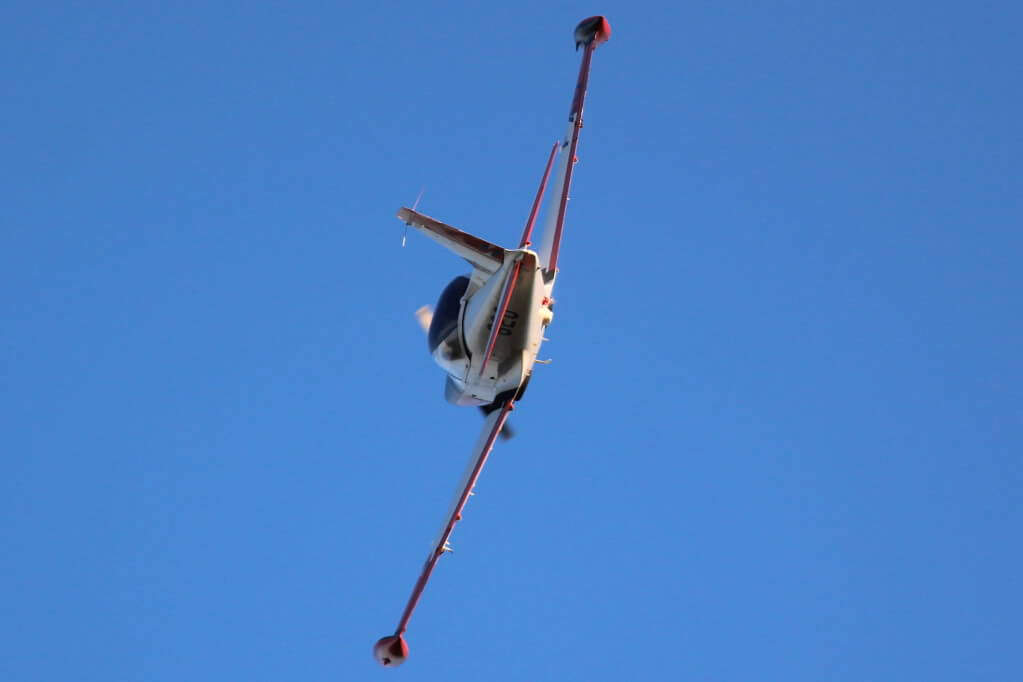
AEROBATICS
Our rate of climb was about 1100 ft/min taking us under for minutes to level off at 4500 ft on the aerodrome overhead and set up the aircraft for some aerobatics thus getting an idea of some of its handling characteristics. We started with a gentle lazy eight demonstrated by my companion followed by my attempt. Entry is at 140 knots with a shallow dive plus a gentle pull up to obtain entry speed again. Reaching a 45 degree turn from the start I was looking to be at a 45 degrees angle of bank, increasing to 90 degrees bank on completion of a 90 degree turn and so forth until completing a full 180 degree. This being a gentle coordination exercise gave a good suggestion of how controllable the aircraft is when compared with the less responsive and slower T-34 (the SF-260EU cruises at the T-34’s VNE!). Power was set back up to 2500 rpm and 25 in HG which gave us a cruising speed of about 140 kt. From this speed steep 2G turns followed at 60 degrees angle of bank provoking aural and visual stall warnings, as back pressure and drag increase whilst airspeed drops in a matter of seconds to 100 kt

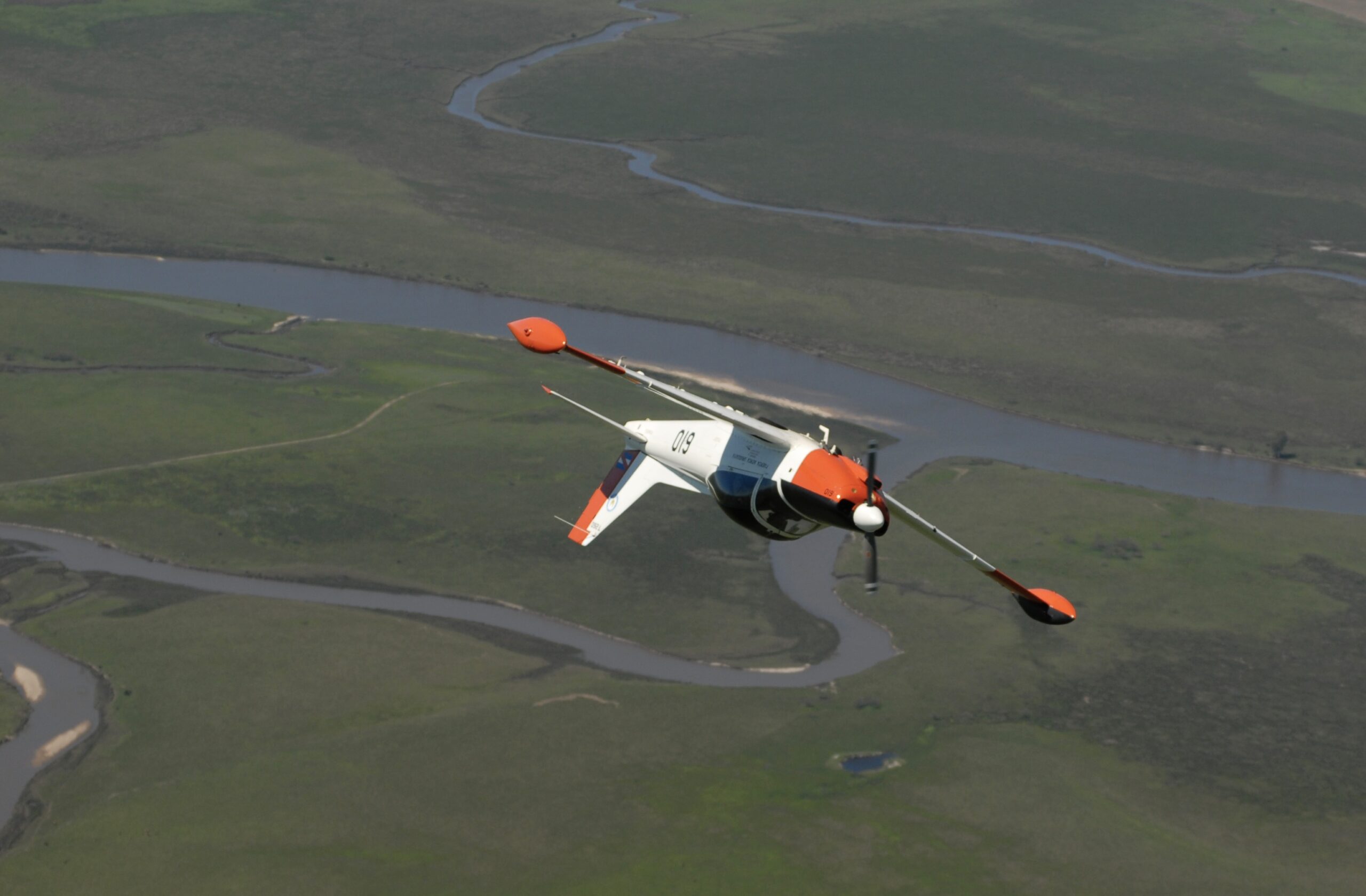
At our weight and angle of bank in a clean configuration the POH warns of a stalling speed of about 96 knots, thus a further 2 in HG manifold pressure is useful to keep Vs in check.
A glance at the G meter (and my stretched out chubby face!) revealed 2 Gs. We set heading towards the nation’s capital, Montevideo, to do some rolls. Lowering the nose to obtain the required 160 kt entry speed, Juan applied 20 to 30 degrees nose up before rolling the plane. He kept the rate of roll constant, and appeared effortless maintaining the nose on a selected reference point on the horizon by use of ailerons, elevators and top rudder to achieve a great roll. The rate of roll is a sharp 180 degrees per second! Loops followed with a faster entry speed of 180 knots. Pitching up from level flight stall aural warning on again as we increase the dynamic loading pulling hard into 3G on the way up. A touch of right rudder needed on the way upwards, some buffet maybe due to the stall strips on the wing’s leading edge (could be confused with elevator stalling) and seeking 70/75 knots whilst you look at “mother earth” upside down.

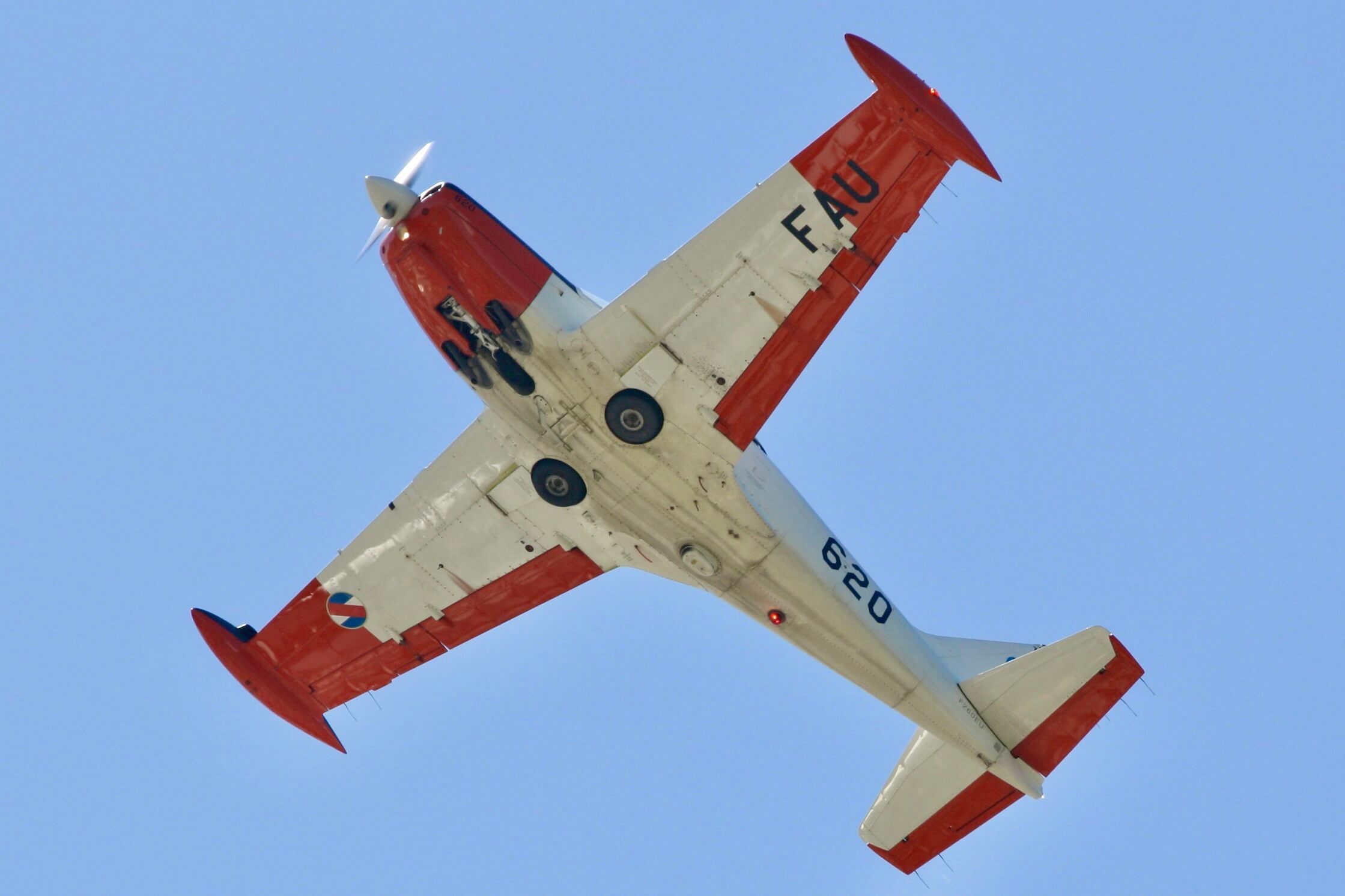
On the way down the clean airframe and wing pick up speed fast, so expediency is required as not to over do your speed, pulling fairly hard to about 3 G once more to exit level at 180 kt. In all exercises a thumb/forefinger usage on the stick is required as the controls are so harmonious and the plane’s envelope handled easily without the use of trim.
The aircraft can accommodate a full range of aerobatics manoeuvres. and is cleared for + 6G/-3G. Expert SF 260 fliers state that the feel of the plane is jet like due to its wing design, control system forces and control surface areas and a good transition platform to fast jets.


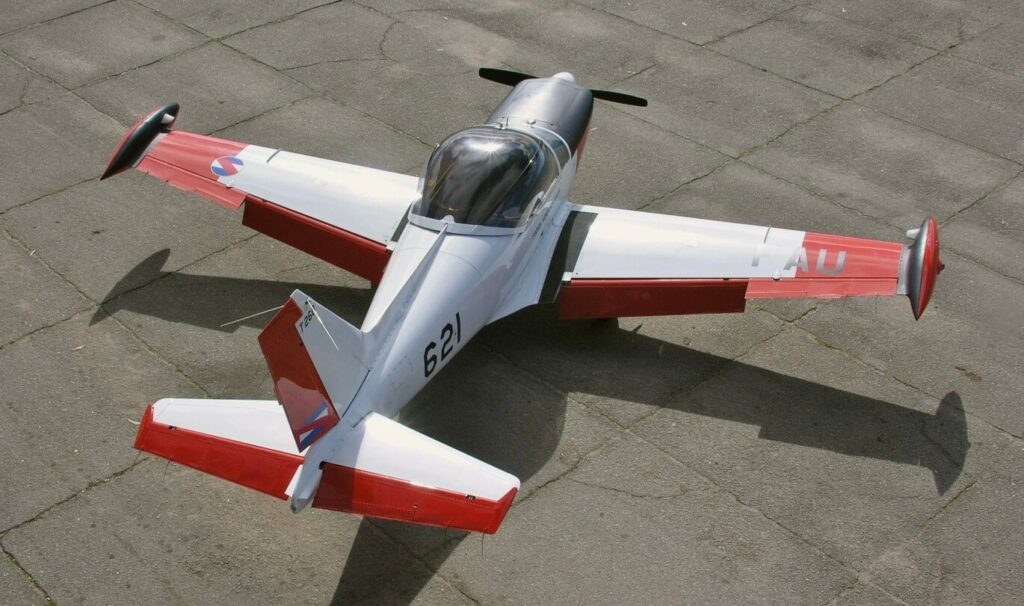
The NACA 64-212 (12% thickness) wing has a short span and surface area (10.10 sq. mts.) and a pronounced positive dihedral angle. It tapers slightly from the leading edge and more distinctively from its trailing edge. The result is less induced drag, further assisted by its faired wing roots and tip tanks, acting as a sort of “whale” like winglet Frise ailerons get rid of adverse yaw; slotted flaps help in delaying the onset stall. Incidentally on the black “non-reflective” inside of the tip tanks forward and above the wing leading edge, small “wing” like aerofoils are fitted. These re energize the airflow over the ailerons at high angles of attack, improving low speed lateral controllability, and reduce the tip tank from bouncing up and down whilst taxiing at full fuel capacity.
Old ideas can be seen on inboard leading edge sections in the shape of stall strips and chordwise vortex creating wing fences further outboard. The fences effectively splitting the wing into separate sections (the leading edge fitted fence is just forward of the ailerons’ hinge line at their inner edge level) and help to prevent spanwise thickening of the boundary layer, thereby tending to better control and stability at the onset of stall.

On the way back, cruising along at 4000 ft. with 23 in HG and 2400 RPM, it was time to dwell with some performance figures. Our indicated airspeed was 130 kts (138 kt TAS) and that would translate to a 16 USG/97 lbs. of fuel burn per hour (book figures) allowing us an airborne time of about 4 hours with full fuel. More endurance can be obtained by proper leaning methods and it is done sporadically (the Aermacchi manual does not recommend leaning below 5000”). The FAU cares for their newly acquired materials and “run in” their new Textron Lycoming AEIO- 540 engines, usually till their reach 50 hours of operation (the manufacturer advises 25 hours) their view is that longer engine life span will be achieved.

The O-540 with its 540 cubic inch displacement is available in no less than 23 different models (AE or aerobatic, I for injected, T for turbo) and with various compression ratios, weights and a decent 1600 hours TBO. The FAU version has a compression ratio of 8.50: 1 and its dry weight is of 175 kg (386 lb) having seen changes in its power section since its original design.
Rejoining the circuit at 1000 ft on the runway heading until reaching a point abeam the tower followed by a break, bank angle to 45 degrees, curved 180 turn into downwind and throttle back or “a la bocina” (to the “horn”) whilst maintaining height. With wings levelled on the downwind leg, prop lever goes full forward. With the airspeed below 125 kt – IAS at which at or below you could lower both the undercarriage and first “notch” of flaps (T/O or 30 degrees) – the gear is down in four/five seconds with slight trim changes, and we get three green lights. Flaps down to T/O (30 degrees), the LG red light and warning horn are now off, Juan reports: “Trebol, gear down and locked, flaps” . I’ll keep 90 kt all the way on downwind and during the base turn to final at approx. 500 ft (POH calls for 100-110 kt at this stage based on a landing weight of 2425 lb/1100 kg).

The shrilling aural warning sounds intermittently when power is reduced to 14 plus/minus 1 in. hg as a reminder to either lower the undercarriage or increase power. A “warning silencer” button is fitted if you don’t carry out none of the above or can’t stand the noise.The sink rate of the laminar flow wing does not produce much lift at low airspeeds. In ideal engine off gliding conditions (in Aermacchi’s parlance: no wind, canopy closed, prop. to “decr. RPM”/coarse pitch, LG up and flaps up) the medium rate of sink is 1000 ft/min at a best glide of 90 kias. At these conditions the airplane would glide 19.5 nm from 12000 ft., 9.75 nm from 6000 ft. and only 3.25 from 2000 ft.This sink rate is higher than the old T-34 thus EMA’s instructors emphasized these data was understood by cadets used to the “Mentor” to maintain safety.
Juan asks for flaps down (LD or 50 degrees) and advises to maintain 85 kt so I trim full aft with my thumb on the stick trim switch. I pointed the nose towards the runway and kept the wings level until gently arresting the descend rate, adopting a fairly flat (and remembered) landing attitude, speed decreased to just above 60 kt and the Italian bailarina quit flying, a touch heavy for my taste as the stall warning horn sounded. You need to remember that the pilot seats low and control the tendency to flare high. The “Go Around” is fairly straightforward, flaps to TO (take-off), elevator trim forward and open up the power, rotation at 65 kt with stick smoothly backwards and the lady flies off at 70 kt. Further landings were carried out without too much trouble, you do get the stall warning at about 73 kias, 10 kias above the published figure of 63 kt (“dirty”) to find the trailing link undercarriage contacting the planet at around 60 kt. The aircraft crosswind limitation for takeoff and landings is 25 knots, a reasonable one for an aircraft of this size.

Achieving higher levels of skill and flying proficiency, at the right cost, is important for many services under ever-decreasing budgets. The FAU latest training aircraft , with its jet like handling, makes it a good stepping-stone to more complex types. It is perfect for teaching aerobatics and formation flying, and is well equipped if not a very stable IFR platform. It has proven to be reliable and by 2014 the fleet had flown 27.000 hours with an average of 1800 hours per year with some aircraft achieving 3000 hours of service; and more than 200 pilots qualified on type. In civilian hands could be a fast tourer and a bagful of fun, so I’ll just keep playing the lottery and praying to fly once more this Ferrari of the Skies!


* If you would like to see more images of the SF-260EU, visit the Image Gallery via this link: Aermacchi SF-260EU Image Gallery
SF.260 HISTORY
Designed by the legendary Italian aeronautical engineer and stylist Stelio Frati, the SF.260 was originally intended as a fast three-seat tourer for the civilian market.The prototype was designated F.250 (F for Frati, 250 for its 250hp Lycoming O-540-AID engine) and combined elements of the fuselage, tail unit and wingtip tanks of Frati’s wood/metal F.15C with the bubble canopy and wings of his all-wood Falco.It was built by Aviamilano, which had manufactured two batches of Falcos, and first flew on July 15, 1964.Two prototype F.260s, with 260hp O-540-E engines, were built under licence from Aviamilano by SIAI-Marchetti, which subsequently purchased the type certificate and manufacturing rights to the aircraft and began series manufacture of the production model SF.260A at Sesto Calende in 1966, subsequently developing it through successive versions as detailed below.SIAI-Marchetti was acquired in 1997 by Aermacchi SpA, which continues to manufacture and market the aircraft.
Some 850 SF.260s of all marks have been built, the majority of them going to military customers.Known military operators have included the forces of Belgium, Bolivia, Brunei, Burkina Faso, Burma (now Myanmar), Burundi, Congo, Dubai, Ethiopia, Haiti, Ireland, Italy, Libya, Mauritania, Mexico, Philippines, Singapore, Somalia, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Tunisia, Turkey, Uganda, Uruguay, Venezuela, Zambia and Zimbabwe.Some surplus military models have reached the civilian market in Europe and the US.Major commercial operators have included Alitalia, Royal Air Maroc and Sabena, which used SF.260s in their flight schools.Total SF-260/SF-260TP fleet time is estimated in excess of 1.7 million flight hours.
SF.260A Initial production version, marketed primarily as a civilian tourer/crew trainer.Following Federal Aviation Authority type approval granted in April 1966, the SF.260 was marketed in the US as the Waco TS-250-3 Meteor, but a planned Franklin 6AS-350A-powered TS-250-3F Meteor 2 variant for the American market did not materialise.
SF.260 B Civilian development incorporating SF.260M (see below) airframe improvements.
SF.260 C SF.260B with increased wingspan.Introduced in 1976.
SF.260 D SF.260C with strengthened airframe, fuel-injected Lycoming IO-540-D4A5 or AEIO-540-D4A5 engine, and MTOW increased to 2,425lb.Introduced in 1985.
SF-260 E Upgraded SF-260D developed in conjunction with Sabreliner Corporation as a contender for the USAF Enhanced Flight Screener requirement, featuring enlarged canopy, modernised cockpit, semi-automatic fuel system, new flap actuators, wing fences, smaller stall sensors, modified flap hinge axis, and MTOW increased to 2,646lb.FAA certified in August 1994.
SF-260 F SF-260E with carbureted engine.
SF.260 MX Prototype for military development of the SF.260, with strengthened airframe and modified cockpit.
SF.260 M Production military version tailored to customer’s requirements with individual designation suffixes, e.g. SF.260 AM (Aeronautica Militare, Italy); SF.260 MB (Belgian Air Force); SF.260 MP (Philippine Air Force), SF.260 MS (Republic of Singapore Air Force); SF.260 MZ (Zambian Air Force).First flown October 10, 1970.
SF.260W Warrior Tactical support/attack development of SF.260M with further strengthened airframe and underwing hardpoints for standard NATO pylons could carry up to 661lbs of stores or drop tanks.First flown in May 1972.Customer designations included SF.260 WD (Dubai); SF.260 WE (Irish Air Corps); SF.260 WL (Libyan Air Force); SF.260 WS (Somali Air Force); SF.260 WP (Philippine Air Force), SF.260 WT (Tunisian Air Force).
SF.260 SW Sea Warrior Dedicated maritime patrol/rescue variant of SF.260 W with provision for carriage of specialized stores such as reconnaissance cameras and parachute-delivered emergency survival packs.
SF.260TP Turboprop version of SF.260M powered by a 350 shp Rolls-Royce (formerly Allison) 250B-17.Prototype first flown July 8, 1980.Structurally identical to piston-engined aircraft aft of firewall except for rudder trim tab.Available as new-build aircraft or turboprop retrofit.
SF 260 EU SPECIFICATION
DIMENSIONS:
Wingspan: 8.35 mts (27.40 ft.)
Length: 7.10 mts (23.30 ft.)
Height: 2.68 mts (8.80 ft.)
ENGINE:
Textron Lycoming AEIO-540-D4A5, six cylinder, horizontally opposed, air-cooled engine. Rated 260 hp @ 2700 rpm. Compression ratio: 8.50:1. TBO: 1600 hours.
PROPELLER: Hartzell HC-C2YK-1BF/F8477-8R, two bladed, all metal, constant speed, crankshaft driven.
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM:28 V DC with a 24 V, 18 amp lead acid battery and a 70 amp engine driven DC alternator.
WEIGHTS:
Basic: 850kg (1874 lbs.)
Typical: (Aerobatic training)2 x crew + wingtips (1/4 full) + full wing tanks = 1140 kg (2514 lbs.)
Training mission: 2 x crew+ full tip tanks = 1190 kg (2634 lbs.)
Ferry mission: 3 x crew + baggage + full wing & tip tanks = 1300 kg (2865 lbs.)
Fuel: 243 lts/64.20 usg (total) = 385.70 lbs/175.31 kg
227 lts/59.97 usg (usable) = 360.32 lbs/163.78 kg
LOAD FACTOR LIMITATIONS:
Utility (3 PAX):
+ 4.4g and– 1.76g (flaps up)
+ 2.5g and 0g (flaps down and/or landing gear extended)
Aerobatic:
+ 6g and – 3g (flaps up)
+ 2.5g and 0g (flaps down and /or landing gear extended).
Limit (clean): + 6 g to Minus 3
AIRCRAFT CATEGORIES:
Aerobatic – 1 to 2 persons in front seats.
Baggage compartment maximum load: 33 lbs (15 kg) for aerobatic category. f
For utility category 44 lbs (20 kg)
Utility – 1 to 3 persons
Baggage compartment maximum load: 44 lbs. (20 kg)
Aerobatics maneuvers permitted in utility category are: chandelle, lazy eight, steep turns and stalls.
SPEEDS – IAS unless stated:
Vr 65 kt
Vfe 125 kt
Vfe (full flaps down) 110 kt
Vle 125 kt
Vno 187
Vmo 182 kt (aeros) + 156 kt (utility)
Vne 236 kt
Manufacturer: ALENIA AERMACCHI (Venegono, Varese, Italy)
Web: https://www.leonardo.com/en/news-and-stories-detail/-/detail/alenia-aermacchi-sf-260-900-and-still-going-strong
BRIEF HISTORY OF THE ESCUELA MILITAR DE AERONÁUTICA

Military aviation beginnings in Uruguay, the second smallest country in South America, dates to 17 March 1913 when the initial batch of 10 Army officers started flying training under the guidance of French aviator Marcel Paillette at Los Cerrillos field near Montevideo with a Bleriot and a Farman biplane. Monsieur Paillette would not renew his contract with the Uruguayan government, after failing to agree salary arrangements, delaying therefore further courses thus the official creation date for the then known Escuela Militar de Aviación(Military Aviation School) is 20 November 1916 with a field at Camino de Mendoza, near Montevideo used as an aerodrome. During those three years of inactivity a few Uruguayan Army officers were sent to Argentine and Chilean Military Aviation Schools to obtain their wings. One of them Captain Juan Manuel Boiso Lanza would become the school first commanding officer and in 1918 Uruguay’s first air martyr, dying on an accident whilst carrying out further training with the French Aviation Militaire in Pau, France. The school airfield would carry his name in his homage as still does, nowadays being the home of FAU Headquarters.
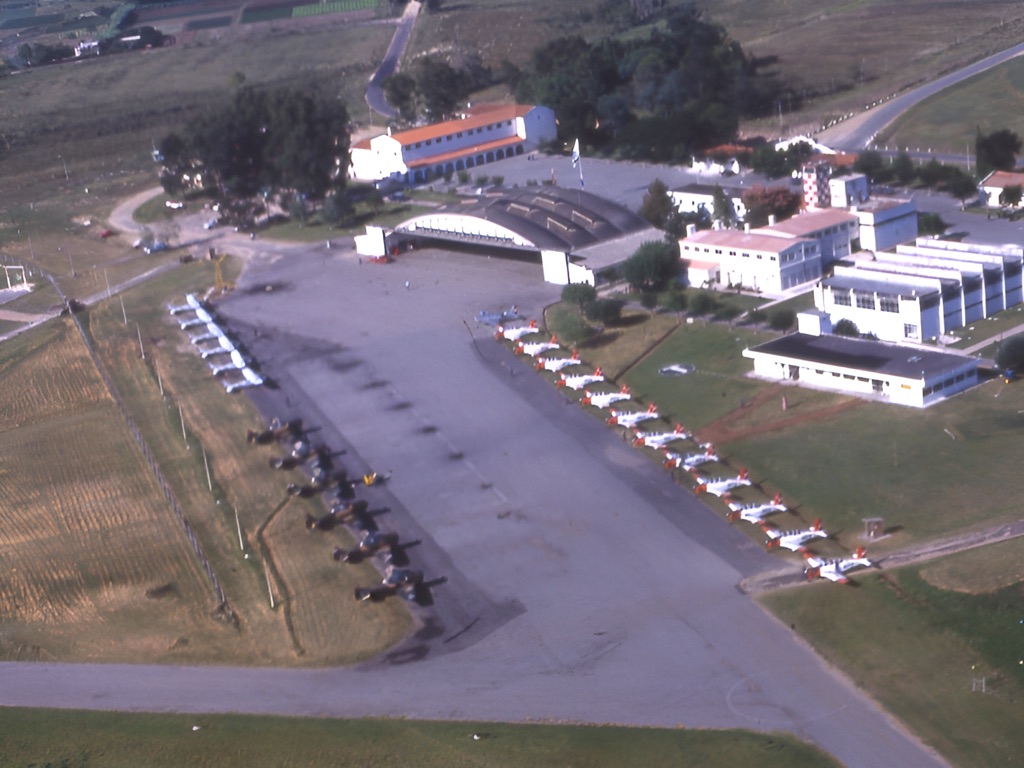

During this pioneering era, the school fleet had a distinct French and British flavour with locally built Castaibert 913-IV and 914-V monoplanes, later joined by Farman biplanes, surplus UK built Avro 504K and Nieuport Ni 83. Men trained by the school opened new air routes, completed air races and endurance flights achieving several records. Their determination paid dividends in 1929 with an Atlantic crossing by Lt. Col. Tydeo Larre Borges and French Captain Leon Challe, on a Breguet 19 single engine aircraft between Spain and Brazil. In 1937 the school changed its name to Escuela Militar de Aeronáutica (Military Aeronautical School ) and came relocation to its actual emplacement in near the town of Pando. The then named Aeródromo Militar General Artigas had been in used since 1928 by the French Aeropostale (a predecessor of Air France)i n postal services via Montevideo using Latecoere 25s. Their old hangar still stands (as a gym for the cadets)having endured visits of high calibre aviators of the like of Saint-Exupery and Jean Mermoz.
The thirties saw new flying materials arriving from the UK in the shape of 18 Tiger Moths. During WW2 days and with credits granted under lend-lease accords with the US, new defence and training materials arrived as Curtiss SNC-1 Falcons, North American AT-6B/D Texans and Fairchild PT-19A. This bonanza continued during the late forties and fifties with further batch of 10 Texans and 10 DHC-1 Chipmunk, preparing the EMA to receive her first students from civilian ranks in 1949 (until then only army/navy staff could join in) and setting the scene to become the “eagles nest” of the newly created, independent air arm, the Uruguayan Air Force (Fuerza Aérea Uruguaya – FAU) in December 1953.
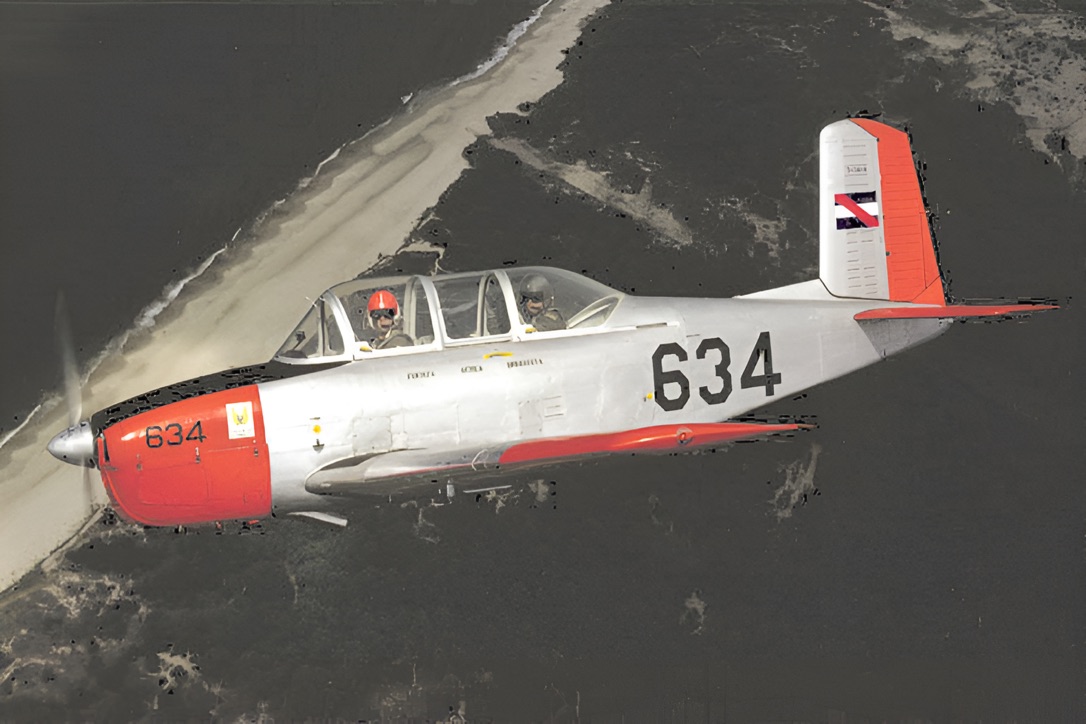

Uruguay was the first country in any South/Central American nation to train women pilots/navigators, the first four ensigns graduated in 1999 (the FAU being the first service in the country to enlist females). Approximately 95 pupils are at the school at one time (less than 10% are women) aspiring to become pilots and navigators during their four year course. The renovated contemporary fleet comprises 12 SF-260s (one was lost on a fatal accident) and two Raytheon B-58 twin-engine aircraft. Cadet pilots can expect to log 120 hours on the Aermacchi before their postings as officers/ensigns to the EVA (Escuela de Vuelo Avanzado – Advanced Flying School) in Durazno, to spend one year flying the Swiss built Pilatus PC-7, before joining a squadron.





.png)
.png)

